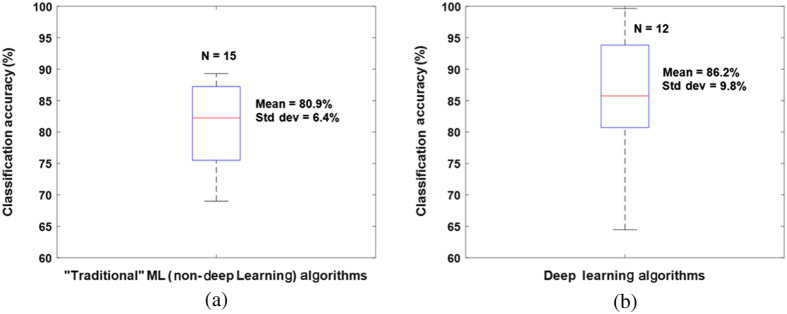
Fig. 7.
Box plots showing the means, standard deviations, and distributions of reported accuracy values from burn wound classification studies using (a) “traditional” (non-deep learning) ML algorithms and (b) deep learning ML algorithms with digital color images as inputs. Classification results from 15 different “traditional” ML algorithms and 12 different deep learning algorithms were used; the data are from Refs. 19–26, 28, 30, 32, 33, 36, 37, 41–43, and 45–47. Several studies comparing multiple ML algorithms21,23,26,33,37,43,45 provided multiple data points that were included in these box plots. Overall, the deep learning algorithms trended toward higher mean accuracy, and the five highest accuracy values were all from deep learning algorithms. However, the deep learning algorithms still had a wide range of reported accuracy values, likely due to the substantial presence of other factors that differed between the studies (e.g., size and composition of dataset; training, validation, and testing procedures; type of ML algorithm employed; types of data pre-processing; and categories used for classification).