Fig. 1. Initial development of a split PE in tissue culture and for AAV-mediated in vivo prime editing.
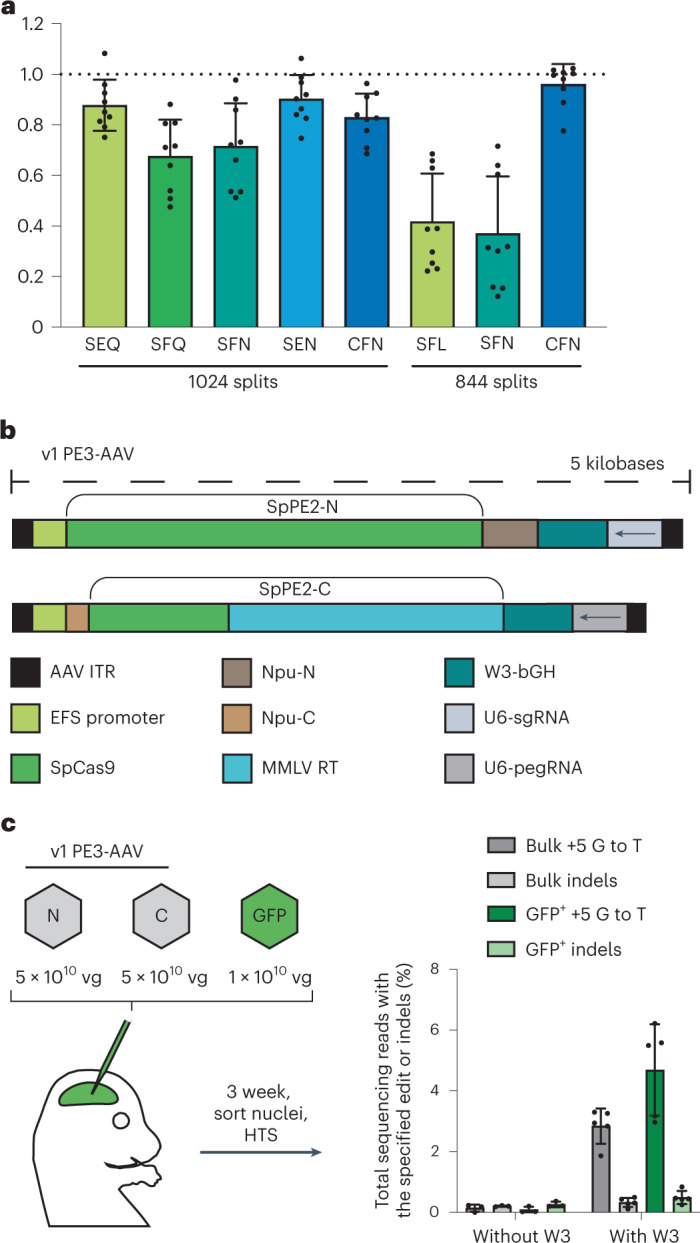
a, Editing performance at three genomic loci of intein-split PE3 variants normalized to that of unsplit, canonical PE3 when delivered by plasmid transfection in HEK293T cells. The split site in SpCas9 and the identity of the three most N-terminal residues of the C-terminal extein are indicated below each bar. A suboptimal amount of editor plasmid was used to avoid saturating editing efficiencies. Dots represent values normalized to canonical PE3 activity, and error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. of n = 3 biological replicates at three genomic loci. b, Schematic of v1 PE3-AAV architecture. c, In vivo editing activity of v1 PE3-AAV9 with pegRNA encoding the Dnmt1 +5 G-to-T edit delivered to neonatal C57BL/6 pups by P0 ICV injection at a dose of 1 × 1011 vg total (5 × 1010 vg per half). Cortex (neocortex and hippocampus) was harvested; nuclei were isolated and sorted by FACS into bulk and GFP+ populations; and genomic DNA was harvested and analyzed by HTS. Dots represent individual mice, and error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. of n = 3–5 mice; each condition includes both male and female mice.
