Fig. 2. AAV-mediated in vivo prime editing efficiency is dependent on the type of edit.
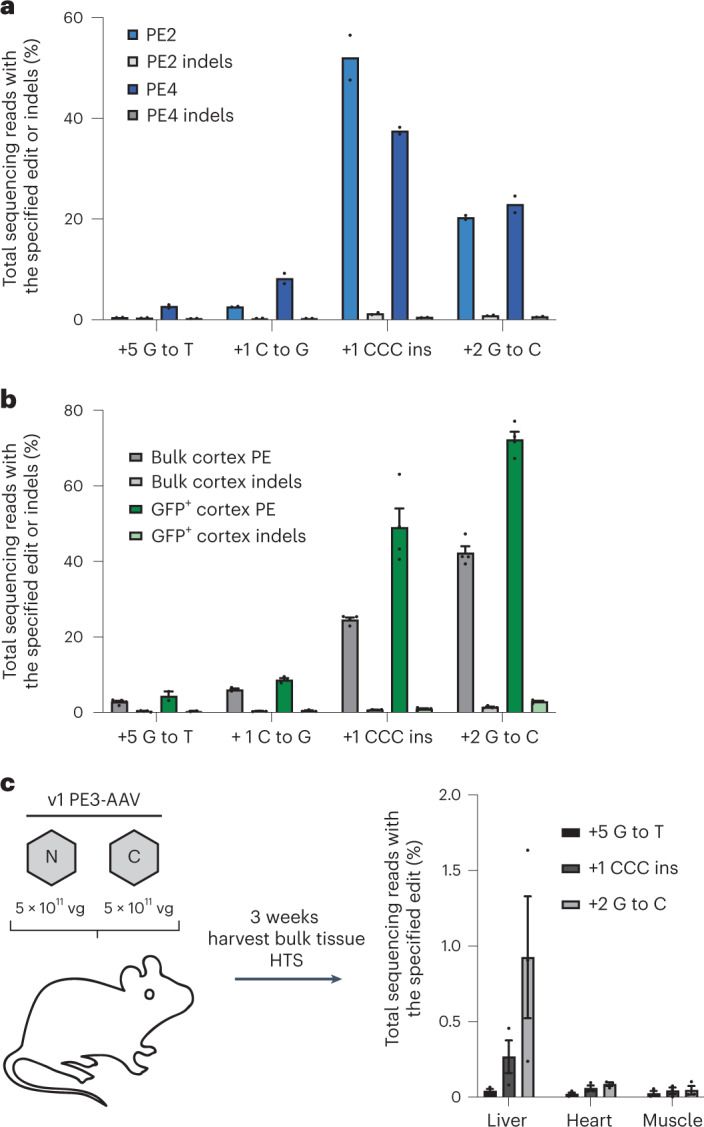
a, Editing activity of PE2 and PE4 in N2a cells by plasmid transfection for four different edits at Dnmt1. N2a cells were transfected with either PE2 and pegRNA or PE4 (PE2 + MLH1dn) and pegRNA. Three days later, gDNA was harvested and analyzed by HTS. Dots represent values, and bars represent means of n = 2 biological replicates. b, In vivo editing activity of v1 PE3-AAV9 delivered to neonatal C57BL/6 pups on P0 by ICV at a total dose of 1 × 1011 vg (5 × 1010 vg per half). Cortex (neocortex and hippocampus) was harvested, nuclei were isolated and sorted by FACS into bulk and GFP+ populations, and gDNA was analyzed by HTS. Dots represent individual mice, and error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. of n = 3–4 mice; each condition includes both male and female mice. c, In vivo editing activity of PE3 delivered via v1 PE3-AAV9 by RO injection to 6–8-week-old C57BL/6 mice at a total dose of 1 × 1012 vg. Three weeks after injection, bulk tissues were harvested and gDNA was isolated and analyzed by HTS. Dots represent individual mice, and error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. of n = 3 mice; each condition includes both male and female mice.
