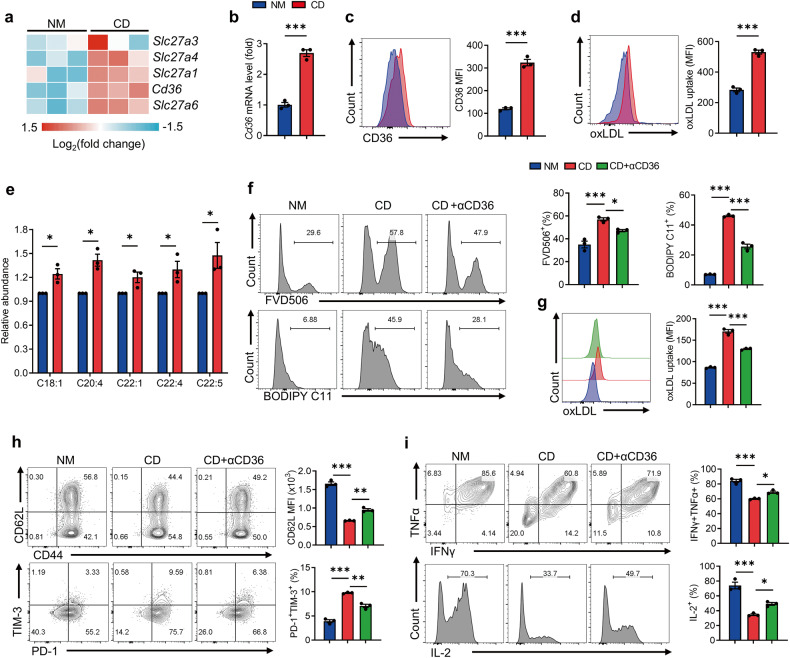
Fig. 5. Cystine deprivation upregulates CD36 which causes lipid accumulation and ferroptosis in T cells.
a RNA-seq analysis of fatty acid uptake-related genes in the indicated T cells (n = 3 per group). b, c RT-qPCR (b) and flow cytometry (c) analysis of T-cell CD36 expression cultured in NM or CD (n = 3 per group). d oxLDL uptake assay of the indicated CD8+ T cells via oxLDL-DyLight 488 staining (n = 3 per group). e Polyunsaturated fatty acid levels in the indicated CD8+ T cells (n = 3 per group). f CD8+ T cells were cultured in NM, CD, or CD + αCD36 medium for 72 h (n = 3 per group). The levels of cell death and lipid peroxidation in the indicated T cells were assessed by flow cytometry. g, h Flow cytometry analysis of the oxLDL uptake (g), the percentages of CD44+CD62L+ subset, and PD-1+TIM-3+ subset (h) of the indicated T cells. i IFNγ, TNFα and IL-2 secretion of the indicated T cells. Each symbol represents one individual. Data are mean ± s.e.m. p values are measured by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test (b–e) and one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test (f–i). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.