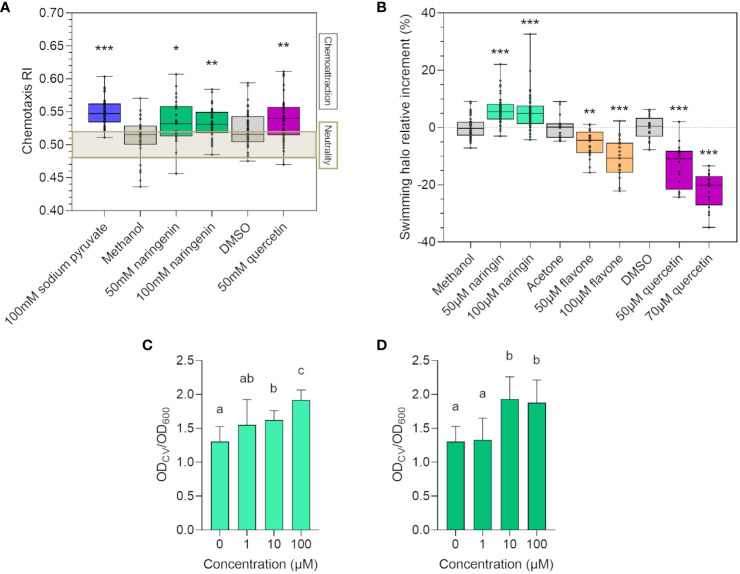
Figure 2.
Flavonoids affect P. xenovorans LB400 chemotaxis, motility, and biofilm formation abilities. (A) Chemotaxis of strain LB400 toward flavonoids on gradient plates after 72 h of growth at 30°C is quantified by calculating the chemotaxis response index (RI). RI higher than 0.52 indicates chemoattraction, RI lower than 0.48 indicates repulsion, whereas 0.48 < RI < 0.52 indicates neutral behavior. Statistical analysis was carried out on at least three independent experiments using ANOVA followed by Tukey–Kramer post-hoc test (*p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001). (B) Percentage of relative increase of the swimming halo diameter of strain LB400 was calculated as described by Wang et al. (Wang et al., 2019). Statistical analysis was carried out on at least three independent experiments using Dunn’s post-hoc test (*p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001). The graphs (C, D) report the relative biofilm formation ability of strain LB400 in the presence of the flavonoids naringin (C) and naringenin (D) expressed as the ratio between the OD600 value for crystal violet staining and the OD600 indicating bacterial growth, as described in the material and methods section. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using Dunn’s post-hoc test, and letters indicate statistically different groups (p ≤ 0.05).