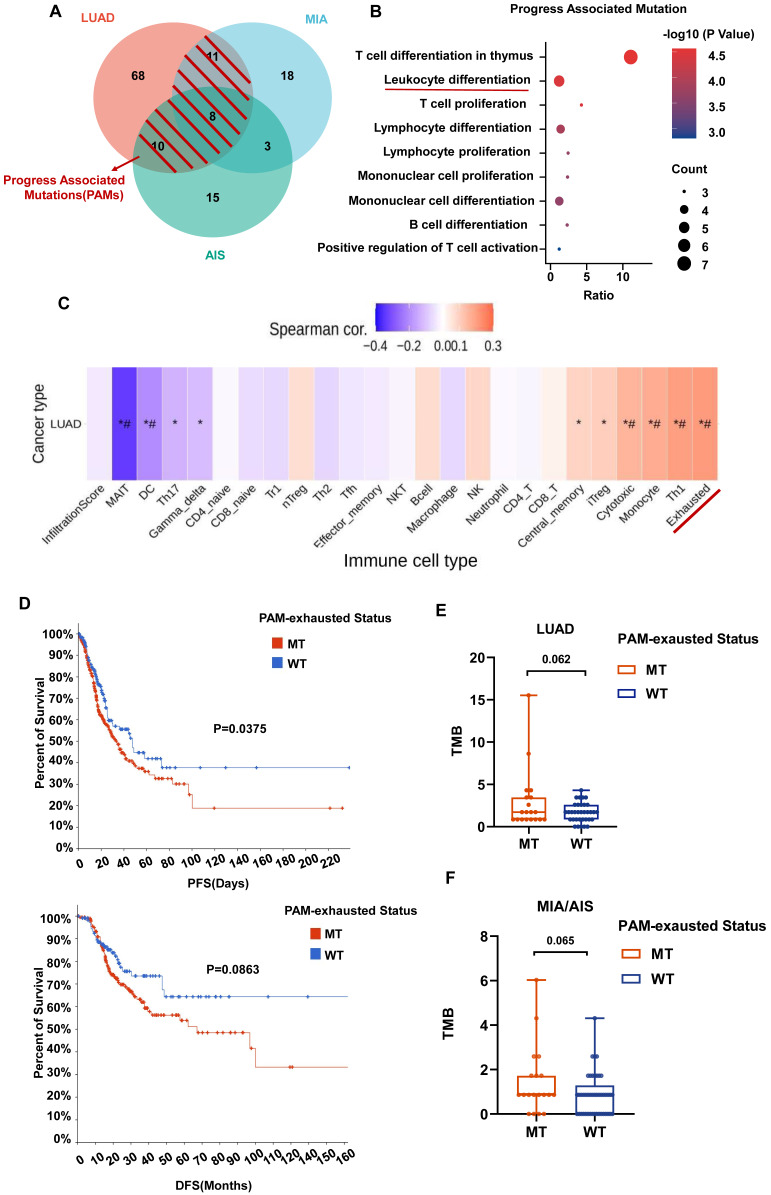
Figure 6.
The role of PAM in the tumor microenvironment (TME) and clinical prognosis. A. Venn plot showing different and shared genetic mutations in all subtypes of LUAD. The parts highlighted in red represent progress-associated mutations (PAMs). B. Bubble plot of PAMs enrichment analysis in immune-related pathways. B. Correlation heatmap between exhaustion-related mutation (PAM-exhausted) and all immune cell subtypes. PAM-exhausted gene: CARD11, DNMT3A, MUC16, RBM10, TRRAP, ZFHX4. D. Analysis of PAM-exhausted and wild-type (WT) for progression-free survival (PFS)(upper) and disease-free survival (DFS)(under). E, F. TMB levels comparison of PAM-exhausted and WT in LUAD (E) and MIA/AIS (F).