Fig. 4.
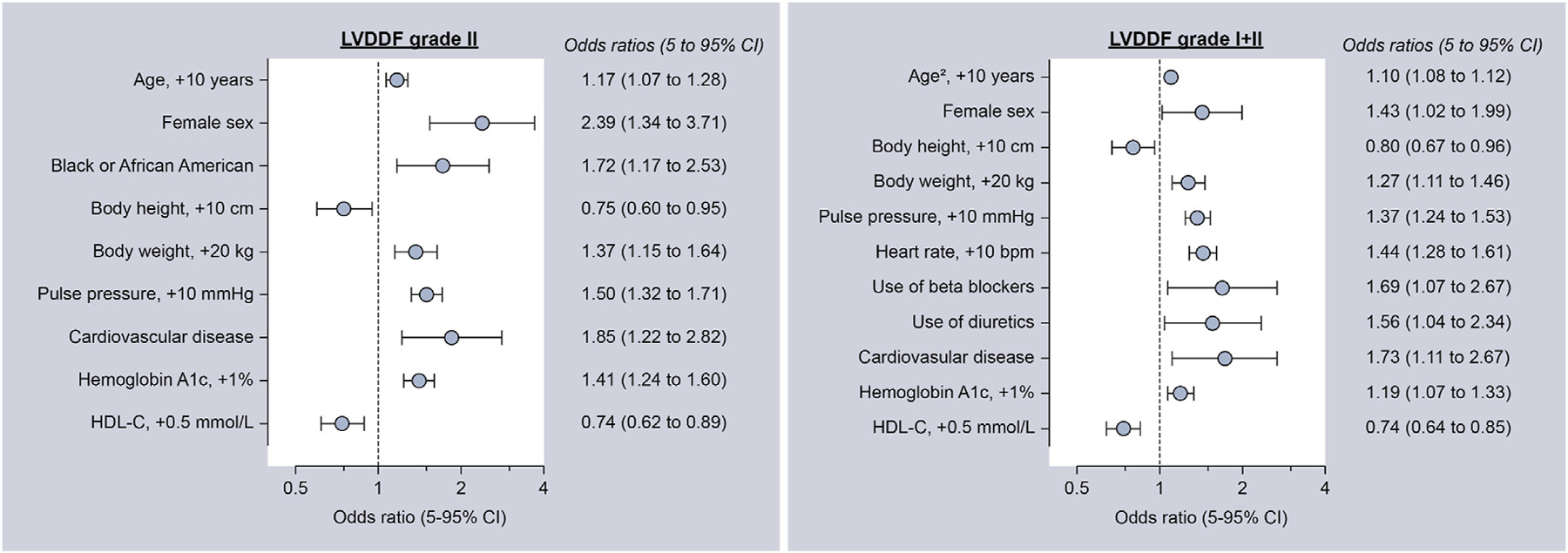
Clinical correlates of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction. Variables considered included age, age,2 sex, race, smoking status (never smoker, past smoker, and current smoker), body height and weight, pulse pressure, heart rate, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, COPD, eGFR, cardiovascular disease, type of antihypertensive medication (beta-blockers, diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blocker, and alpha antagonists), lipid-lowering drugs, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HbA1c and triglycerides. ACE, angiotensin-converting-enzyme; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; LVDDF, left ventricular diastolic dysfunction.
