FIGURE 4. HOXB13 expression in advanced castration resistant prostate cancer.
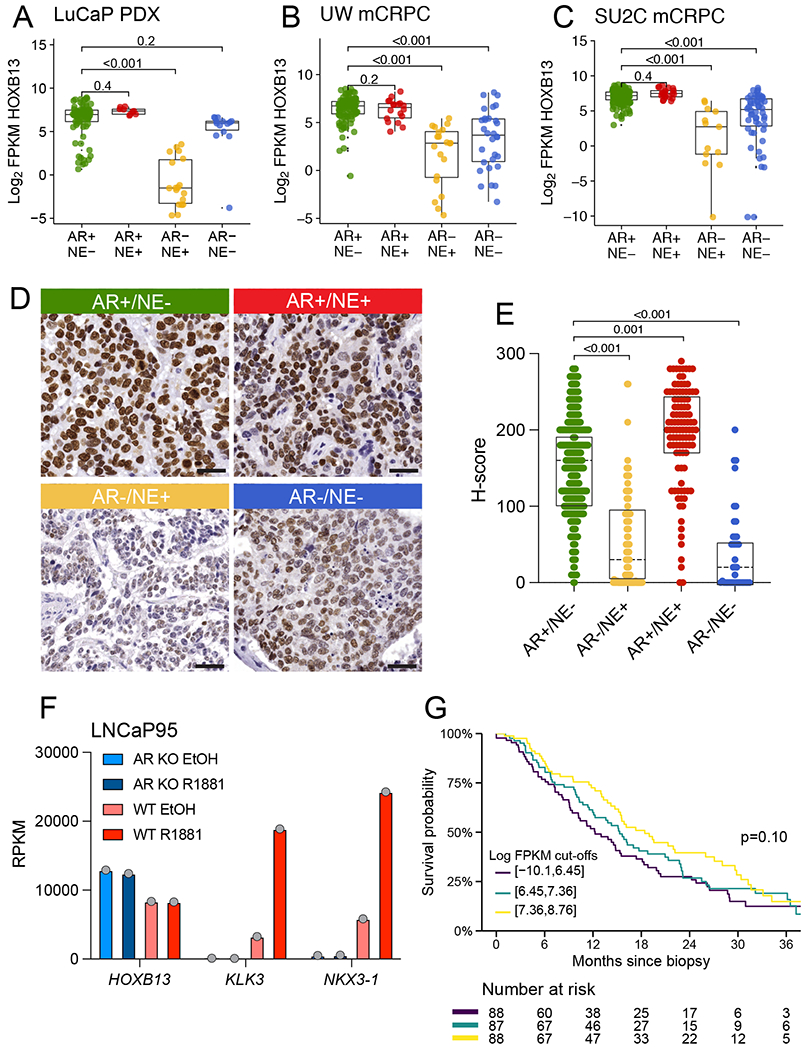
HOXB13 mRNA expression across molecular subtypes of CRPC (AR+/NE−, AR+/NE+, AR−/NE+, AR−/NE−) in A. PDX tissues (N=121 samples from 54 PDX lines), B. University of Washington rapid autopsy (TAN) cohort (N=185 samples from 98 patients) and C. the SU2C-IDT (N=270 samples from 266 patients). D. Representative micrographs showing HOXB13 protein expression in UW-TAN tissues. E. Boxplot showing HOXB13 IHC H-scores across molecular subtypes. F. HOXB13, KLK3 and NKX3.1 mRNA expression analyses in wild type (WT) and AR knock out (ARKO) LNCaP95 cells treated with vehicle (EtOH) or the synthetic androgen R1881 demonstrate the AR− and androgen-independence of HOXB13 levels G. Kaplan-Meier plots shows overall survival in the SU2C cohort stratified by HOXB13 expression. Colored lines indicate tertiles of HOXB13 log2 FPKM.
