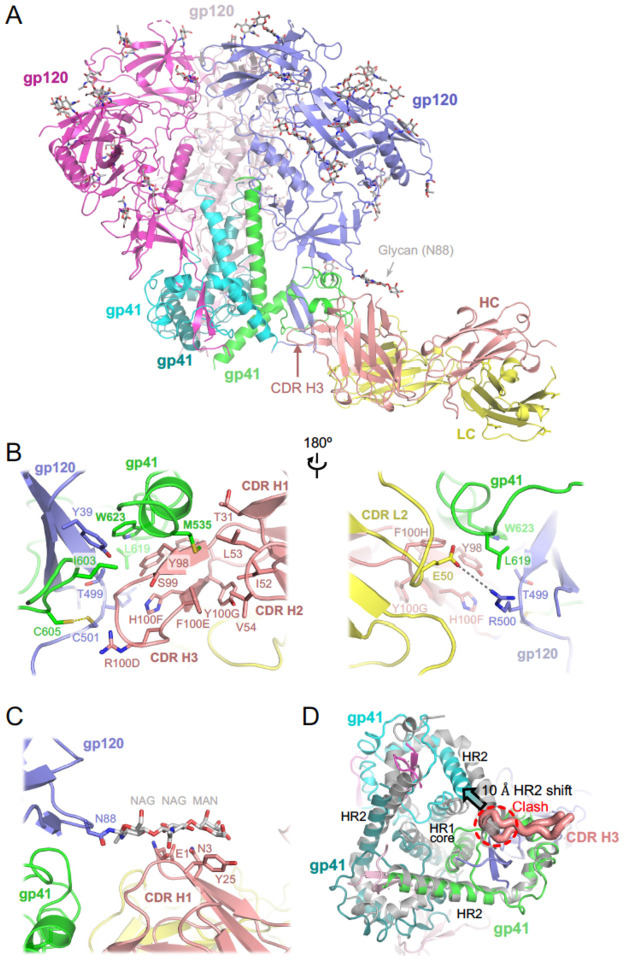
Figure 2. Cryo-EM structure of HIV-1 Env BG505 SOSIP.664 construct in complex with ELC07 Fab.
(A) Overview of the atomistic model. The protein chains are shown as cartoons, with individual subunits indicated and colour-coded: gp41 in green, cyan, and teal; gp120 in blue, light pink, and bright magenta; ELC07 heavy chain (HC) and light chain (LC) in salmon and yellow, respectively. The glycans are shown as sticks with carbon atoms in grey. Arrowheads indicate the glycan attached to Asn88 of the gp120 subunit interacting with the antibody and the CDR H3 loop of the heavy chain.
(B) A zoomed view on the Env-ELC07 interface shown in two orientations related by a 180° rotation. Side chains of residues discussed in the text are indicated and shown as sticks. ELC07 heavy chain residue numbering follows the Kabat conventions. Yellow dash indicates the designed SOS bond between gp120 Cys501 and gp41 Cys605; grey dash indicates a salt bridge between gp120 Arg500 and ELC light chain Glu50.
(C) Zoomed view on Ans88-linked glycan and its interface with ELC07.
(D) Structural changes in the HIV-1 Env induced by ELC07 binding revealed by superposition with 3-fold symmetric BG505 SOSIP.664 (PDB ID 4TVP, shown as grey cartoons)47; viewed from the base of the Env ectodomain. CDR H3 is shown as thick ribbon and indicated, with the rest of the Fab structure hidden for clarity. The heptad repeats 1 and 2 (HR1 and HR2) of gp41 subunits are indicated. Insertion of CDR H3 loop is made possible by ~10 Å shift (indicated by arrowhead) of HR2 belonging to the gp41 chain engaged by the antibody. The position of HR2 complying with the expected 3-fold symmetry is not possible due to a clash with CD HR3 (indicated).