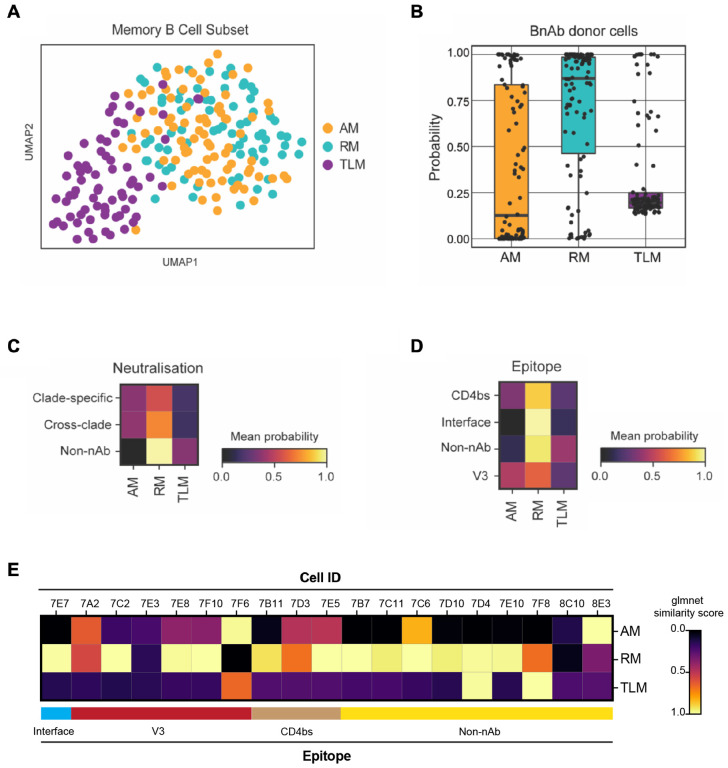
Figure 4: Single B cells from a bnAb donor have a transcriptional phenotype most similar to resting memory cells, irrespective of their BCR specificity or functionality.
(A) UMAP visualisation of single-cell transcriptomes (Smart-Seq2) from 223 IgG+ B cells from an individual living with HIV-1 with low VL (100 c/mL at the time of sampling), coloured by their original FACS sorting strategy as resting memory (RM; cyan), activated memory (AM; orange) and tissue-like memory (TLM; purple).
(B) Similarity of single-cell transcriptomes of HIV-1 Env reactive IgG+ B cells from the bnAb donor with RM, AM and TLM IgG+ B cell subsets from the low VL donor memory B cell subsets, calculated as a probability using the Glmnet algorithm.
(C-D) Heatmaps of the mean probability (as calculated in B) of HIV-1 Env reactive IgG+ B cells from the bnAb donor for memory subsets based on (C) BCR neutralisation of clade C specific or cross-clade HIV-1 PVs or no neutralisation (non-nAb) and (D) BCR epitope targeted on the HIV-1 Env. The BCR specificity and functionality were characterised based on the behavior of soluble mAb cloned and expressed from single B cells from the bnAb donor.
(E) Heatmaps of the mean probability (as calculated in B) of each memory subset for each epitope mapped HIV-1 Env reactive IgG+ B cell from the bnAb donor.