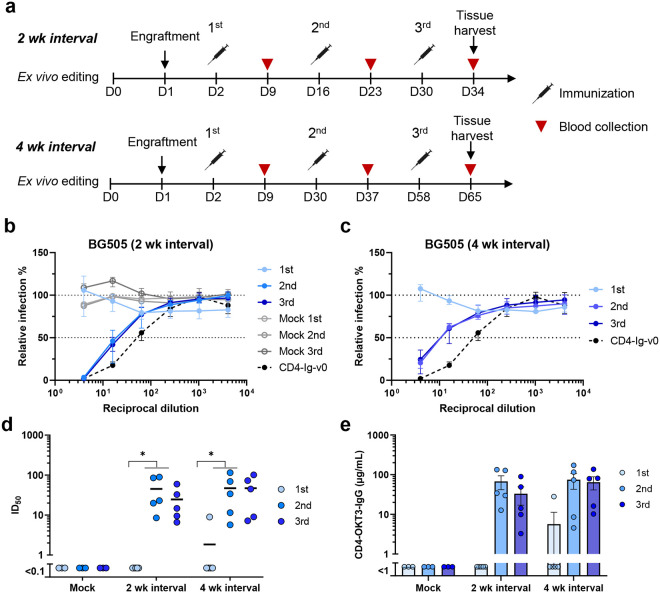
Fig. 2. Engineered B cells generated neutralizing responses in immunized mice.
a Schedule of immunization and blood collections from mice analyzed in subsequent figures. Naïve B cells from CD45.1 donor mice were engineered ex vivo and 5 million cells per mouse were adoptively transferred to CD45.2 recipient mice 24 h later. Mice were immunized with SOSIP-TM (16055-ConM-8.1) mRNA-LNP on two-week (2 wk, Day 2, 16, and 30, n = 5) or four-week (4 wk, Day 2, 30, 58, n = 5) intervals, and serum was collected seven days after each immunization. Spleens and lymph nodes were harvested four days after the final immunization and B cells isolated from these tissues were analyzed by flow cytometry and next-generation sequencing (NGS). b, c Neutralizing responses of sera from mice immunized with SOSIP-TM mRNA. Sera from mice immunized at two-week (b) or four-week (c) intervals were measured individually for their ability to neutralize BG505 HIV-1 pseudovirus in TZM-bl cell assays. Sera from mice (n = 3) engrafted with unedited CD45.1 B cells and immunized on two-week interval (grey dots) served as negative controls. 100 μg/ml CD4-Ig-v0 combined with normal mouse serum served as a positive control. Dots and error bars indicate median and interquartile range for each group. d A summary of the 50% inhibitory dilutions (ID50) of sera from each immunized mouse in b and c. Statistical significance was determined using repeated-measures two-way ANOVA with Geisser-Greenhouse correction. e Serum concentration of CD4-OKT3-IgG after each immunization, measured by ELISA with an anti-CD4 antibody and CD4-OKT3-IgG as the standard.