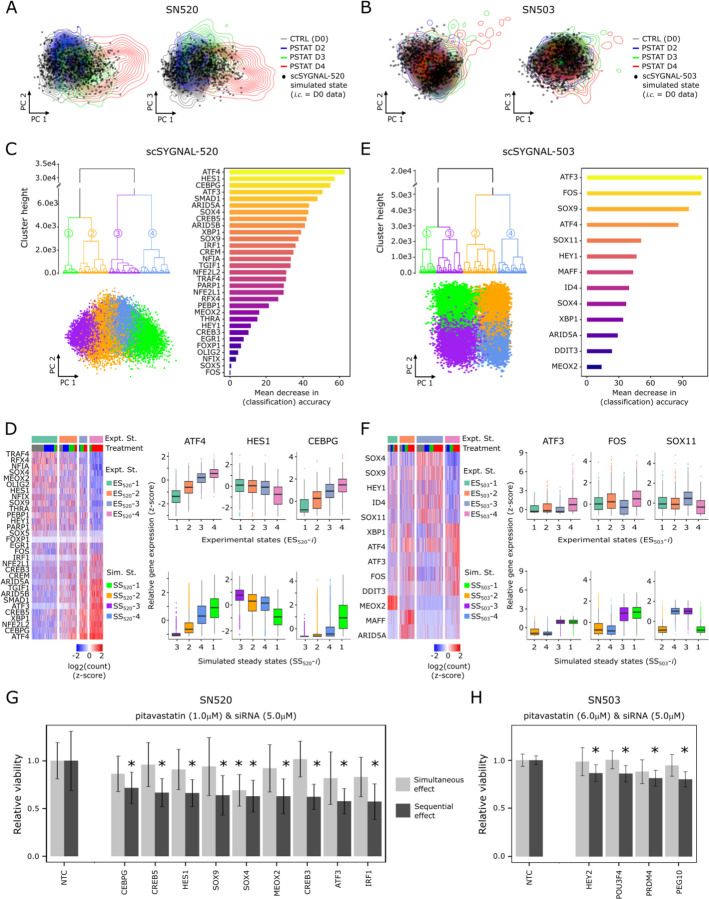
Fig. 6. Dynamic simulations of core TF regulatory network supports phenotypic plasticity of GSCs.
Simulated transcriptional states (black circles) projected along first two principal components. Contour lines represent distribution of PCA scores of TF expression states (core TFs only) for (A) SN520 and (B) SN503 cells. One thousand simulated states were generated using core TF network topologies and corresponding D0 scRNA-seq data for initial conditions (i.c.) as RACIPE inputs. (C) Three plots summarizing results from 1 million RACIPE simulations (independent of (A)) using the core TF-TF network derived from scSYGNAL-520 and randomized initial conditions to explore plausible steady states supported by the network topology. Dendrogram of four distinct simulated steady states. Scatter plot of simulated states projected along first two PCs. Horizontal barplot of rank-ordered TFs based on their importance in distinguishing the four simulated states. Here, importance is defined by the mean decrease in classification accuracy following TF removal from the model, per random forest analysis. (D) Heatmap of expression for SN520 core TFs. Cells (columns) were hierarchically clustered to define experimental states (ES520-i), providing a basis of comparison for simulated states (SS520-i). Adjacent boxplots of three TFs having high importance in random forest classification. Boxplots (top row) of TF expression distributions for experimental states. Boxplots (bottom row) of simulated TF expression distributions (normalized). (E – F) Corresponding simulation results for SN503. (G) SN520 cell viability following 4-day treatment with either simultaneous treatment with pitavastatin and siRNA (light grey bars) or sequential pitavastatin then siRNA-mediated KD of TFs (dark gray bars). Viabilities are relative to non-template control (NTC)-treated cells. (H) Corresponding bar plots of relative viability for SN503. Asterisks (G – H) indicate significant decrease relative to corresponding NTC treatment (FDR p-values ≤ 0.1).