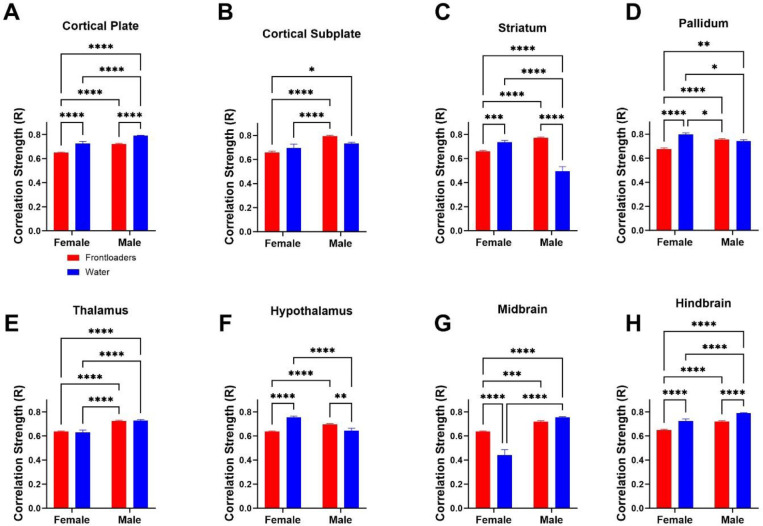
Figure 3.
Correlation strength (R value) is compared across groups and sex within anatomical subdivisions. In most anatomical divisions, the strength of correlation is decreased in female frontloaders as compared to water drinkers. This was true in all divisions except for the cortical subplate, thalamus (no differences), and midbrain (where frontloading increased co-activation). Further, there were main effects of sex in all divisions except for the pallidum, with interactions of sex indicated in many divisions. These results suggest that correlation strength is altered differently between sexes, with male frontloaders showing higher R values in all anatomical divisions than female frontloaders.