FIGURE 6.
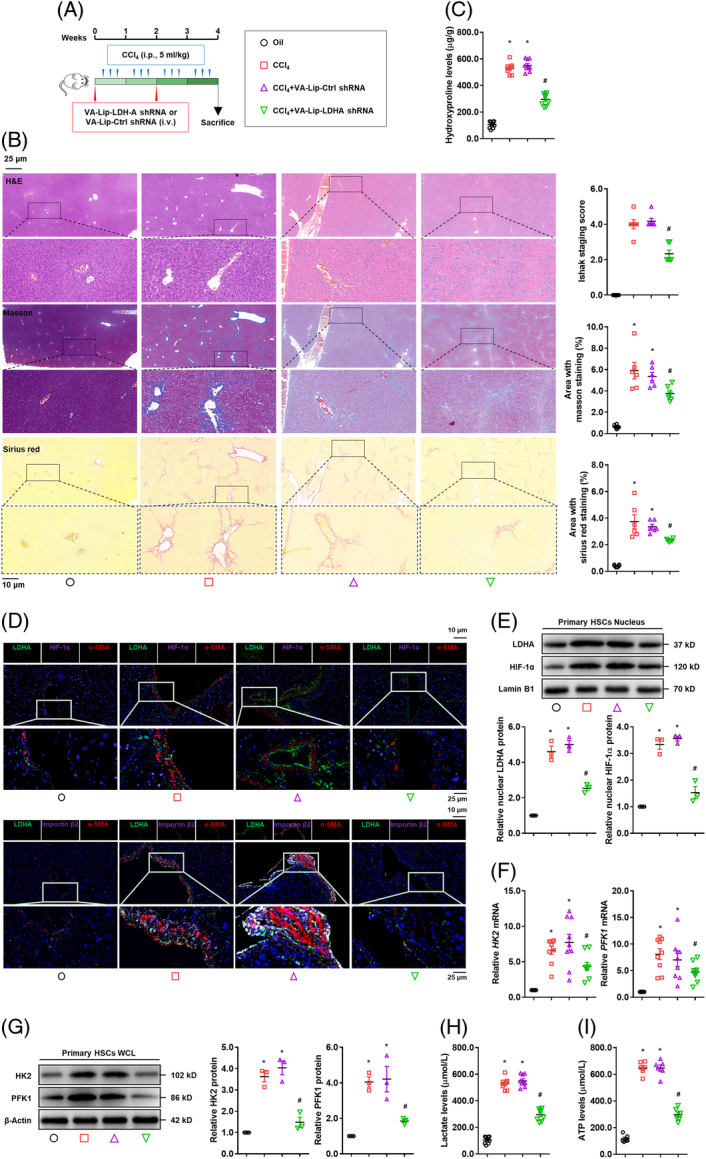
Hepatic-specific deficiency of LDH-A mitigates liver fibrosis and inhibits HSC glycolysis. Mice were intravenously administrated vitamin A-liposome-LDH-A shRNA accompanied by CCl4-induced liver fibrosis (n = 10). (A) Scheme of the experiments. (B) Examinations of liver histopathology and collagens using HE staining, Masson staining, and Sirius red staining with Ishak stage scoring and quantification of positive staining area. (C) Measurement of hepatic hydroxyproline contents. (D) Immunofluorescence analysis of expression and localization of LDH-A, HIF-1α, importin β2, and α-SMA in liver tissues. The nucleus was stained with DAPI. (E–I) Mouse-primary HSCs were isolated for molecular examinations. Western blotting analysis of nuclear abundance of LDH-A and HIF-1α with quantification (E); real-time PCR analysis of mRNA expression of HK2 and PFK1 (F); Western blotting analysis of protein expression of HK2 and PFK1 with quantification (G); measurement of intracellular lactate levels (H), and intracellular ATP levels (I). For this figure, *p<0.05 versus oil, # p<0.05 versus CCl4+VA-Lip-Ctrl shRNA. Abbreviations: α-SMA, α-smooth muscle actin; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; HK2, hexokinase 2; LDH-A, lactate dehydrogenase A; PFK1, phosphofructokinase 1; shRNA, short hairpin RNA.
