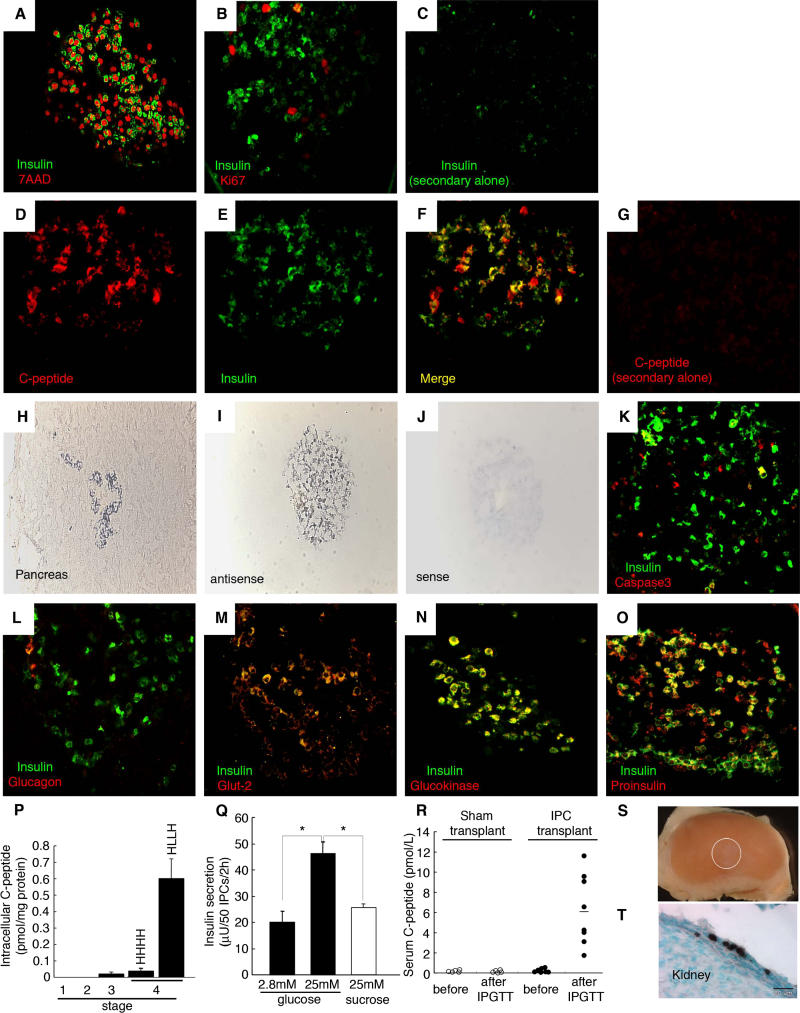
Figure 4. Stage 4 IPCs Express Characteristic Pancreatic β-Cell Markers and Are Glucose-Responsive.
(A–C) Immunofluorescent images of stage 4 IPCs were obtained by confocal microscopy and are representative of at least ten samples for each probe. Shown is simultaneous immunofluorescent staining of insulin and either the nuclear marker 7AAD (A) or Ki67 (B). (C) Lack of immunostaining upon omission of the anti-insulin primary antibody.
(D–G) Detection of insulin C-peptide in cells stained by anti-insulin antibodies. There is complete overlap between immunostained C-peptide and insulin in the cytoplasm.
(H and I) Representative in situ hybridization with antisense riboprobes specific for human insulin on sectioned human fetal pancreatic islet cells (H) or a stage 4 IPC cluster (I).
(J) Sense control probe in situ hybridization on a stage 4 IPC cluster.
(K–O) Simultaneous immunofluorescent detection of insulin and cleaved caspase-3 (K), glucagon (L), Glut-2 (M), glucokinase (N), or proinsulin (O).
(P) Intracellular C-peptide content of IPCs during stages 1–4 by human C-peptide-specific ELISA.
(Q) In vitro secretion assay of stage 4 IPCs. Insulin release followed a step increase from 2.8 mM to 25 mM glucose, but not following exposure to 25 mM sucrose, which served as an osmotic control. *, p < 0.001.
(R) Serum human C-peptide detection 2-wk after sham or IPC cluster transplantation in NOD scid mice. Samples were obtained before or 30 min after intraperitoneal glucose challenge (IPGTT).
(S) Lack of tumor growth after renal transplantation of stage 4 IPCs (graft indicated by white circle).
(T) Immunohistochemical detection of human C-peptide expression in stage 4 IPCs (cells stained brown) 2-wk after engraftment; bar is 20 μm.
Original magnification of (H–J) and (T) was 250×. All other photomicrographs' original magnification was 630×.