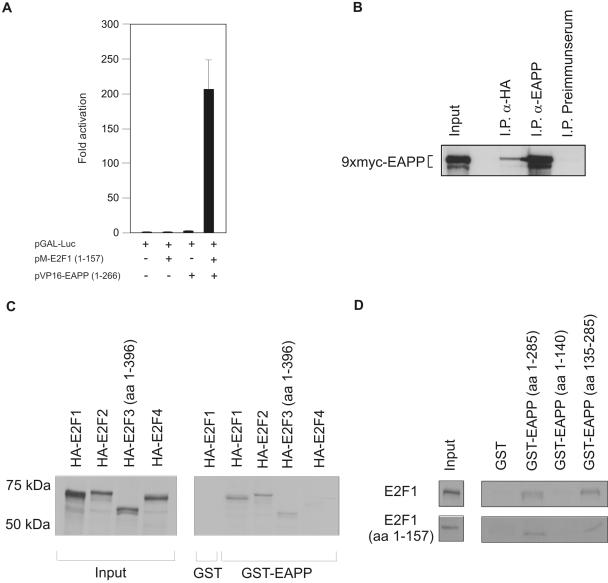
Figure 4.
Interaction of E2F proteins with EAPP. (A) Mammalian two-hybrid assay in U2OS cells. A Gal4-dependent reporter vector (pGAL-Luc) was cotransfected with an expression vector for a GAL-E2F-1 fusion-protein (pM-E2F1; 1–157), a VP16-EAPP fusion-protein (pVP16-EAPP; 1–266), or both. Each bar represents six independent samples adjusted for β-Gal activity. SD is indicated. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of EAPP and E2F-1. 9xMyc-EAPP and HA-E2F-1 were coexpressed in U2OS cells. Immunoprecipitation (IP) experiments were carried out with the anti-EAPP antibody (positive control), an anti-HA antibody (12CA5), and a murine preimmune serum (negative control). Bound proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and coprecipitated Myc-EAPP was visualized by immunostaining with an anti-Myc antibody (9E10). Input means that 1/50 of the amount of cell extract used for the IPs was loaded directly onto the gel. (C) Pulldown assays with GST or GST-EAPP and in vitro–translated 35S-labeled HA-tagged E2F proteins. GST incubated with HA-E2F-1 was used as a negative control. Input means that 1/4 of the amount of in vitro–translated proteins used for the pulldown assays was loaded directly onto the gel. Input- and GST-EAPP bound proteins were visualized by autoradiography. (D) Pulldown assays with GST, GST-EAPP, GST-EAPP(1–140), and GST-EAPP(135–285), and in vitro–translated 35S-labeled E2F-1 (wt or aa 1–157). Input means that one fourth of the amount of in vitro–translated proteins used for the pulldown assays was loaded directly onto the gel. Input- and GST-EAPP bound proteins were visualized by autoradiography.