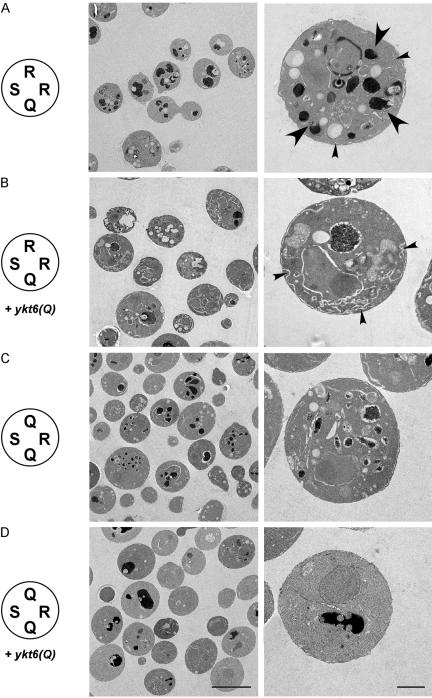
Figure 6.
Morphology of mutant yeast cells expressing sed5(R) as the only version of SED5 as well as compensating mutations in the R-SNAREs SEC22 or YKT6, analyzed by electron microscopy. (A) sed5(R) as sole copy of SED5 (strain YCG15) caused accumulation of large amounts of intracellular membranes (small arrowheads) and fragmentation of vacuoles (large arrowheads). (B) Coexpression of plasmid-encoded ykt6(Q) in the sed5(R) mutant resulted in healthier cells that showed accumulation of membrane cisternae (small arrowheads) but displayed normal vacuole morphology. (C) sec22(Q)/sed5(R) double mutants (strain YCG3) displayed accumulation of fragmented vacuolar structures but lacked anomalous membrane cisternae. (D) sec22(Q)/sed5(R) mutant cells expressing ykt6(Q) in addition to the chromosomal YKT6 gene showed normal (wild-type) morphology.