Figure 5. Neuronal expression of the wild-type Cntnap1 restores myelination and paranodal axo-glial junctions in C324R/− and R765C/− mutants.
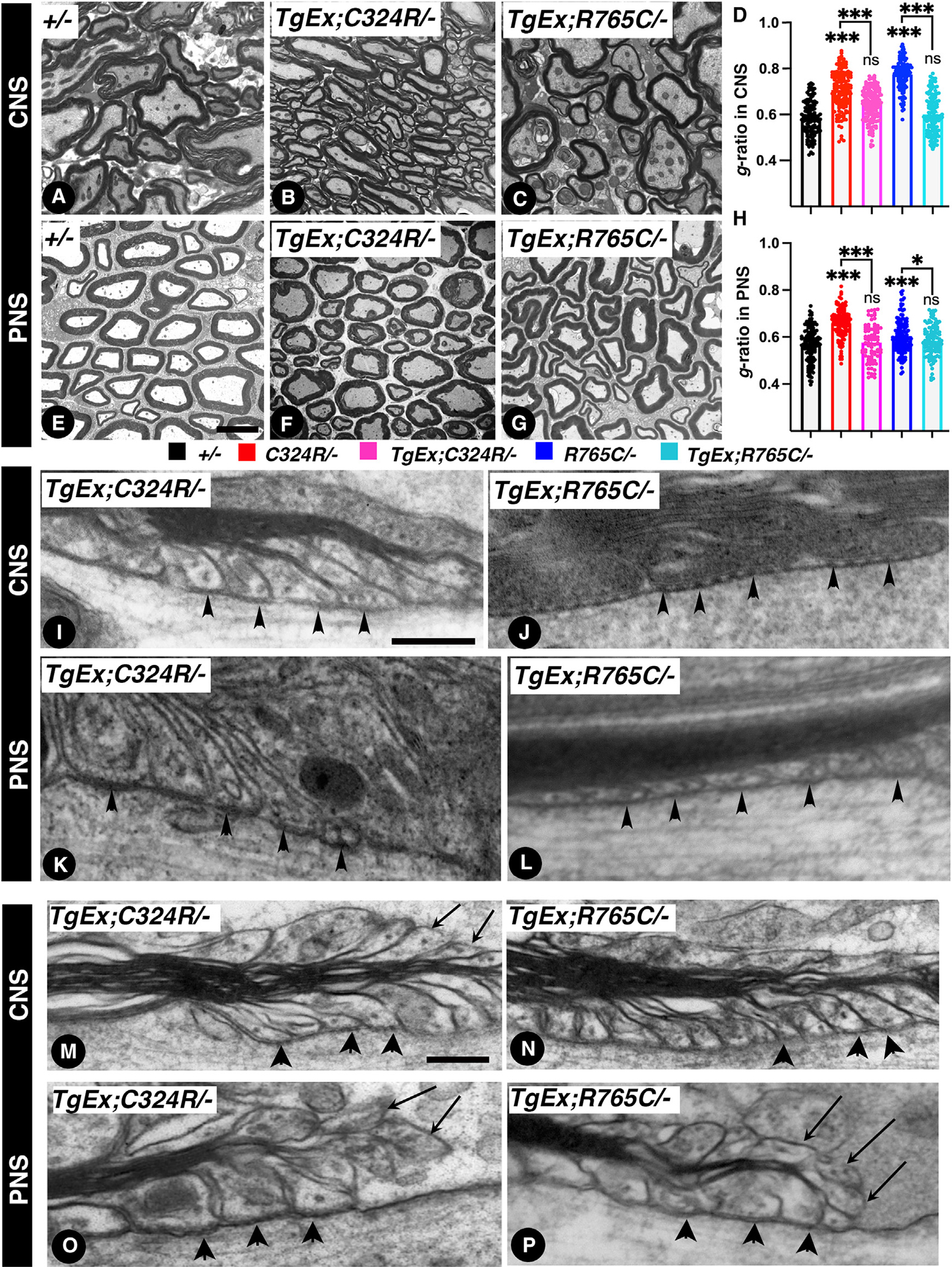
(A–C) 7 weeks after tamoxifen injection, TEM of cross-sections from the spinal cords.
(D) Morphometric analysis showing g-ratios of spinal cord myelinated axons.
(E–G) 7 weeks after tamoxifen injection, TEM of cross-sections from the sciatic nerves.
(H) Morphometric analysis showing g-ratios of sciatic nerve myelinated axons.
(I and J) TEM images of longitudinal sections of spinal cords at the level of the paranodes from 7-week-post-tamoxifen-injection TgEx;C324R/− (I) and TgEx;R765C/− (J). Black arrowheads point to paranodal septa.
(K and L) TEM images of longitudinal sections of sciatic nerves at the level of the paranodes from 7 weeks post tamoxifen injection from TgEx;C324R/− (K) and TgEx;R765C/− (L). Black arrowheads point to paranodal septa.
(M–P) TEM images of longitudinal sections of spinal cords and sciatic nerves. Black arrowheads point to paranodal septa, and black arrows point to everted loops. Scale bars: (A–G) 2 μm; (I–L) 0.2 μm; (M–P) 0.4 μm. Data are represented as the mean ± SEM of three biological replicates.
