Figure 4. Establishment of a CRISPR-CasRx system to specifically modulate m6A-7SK.
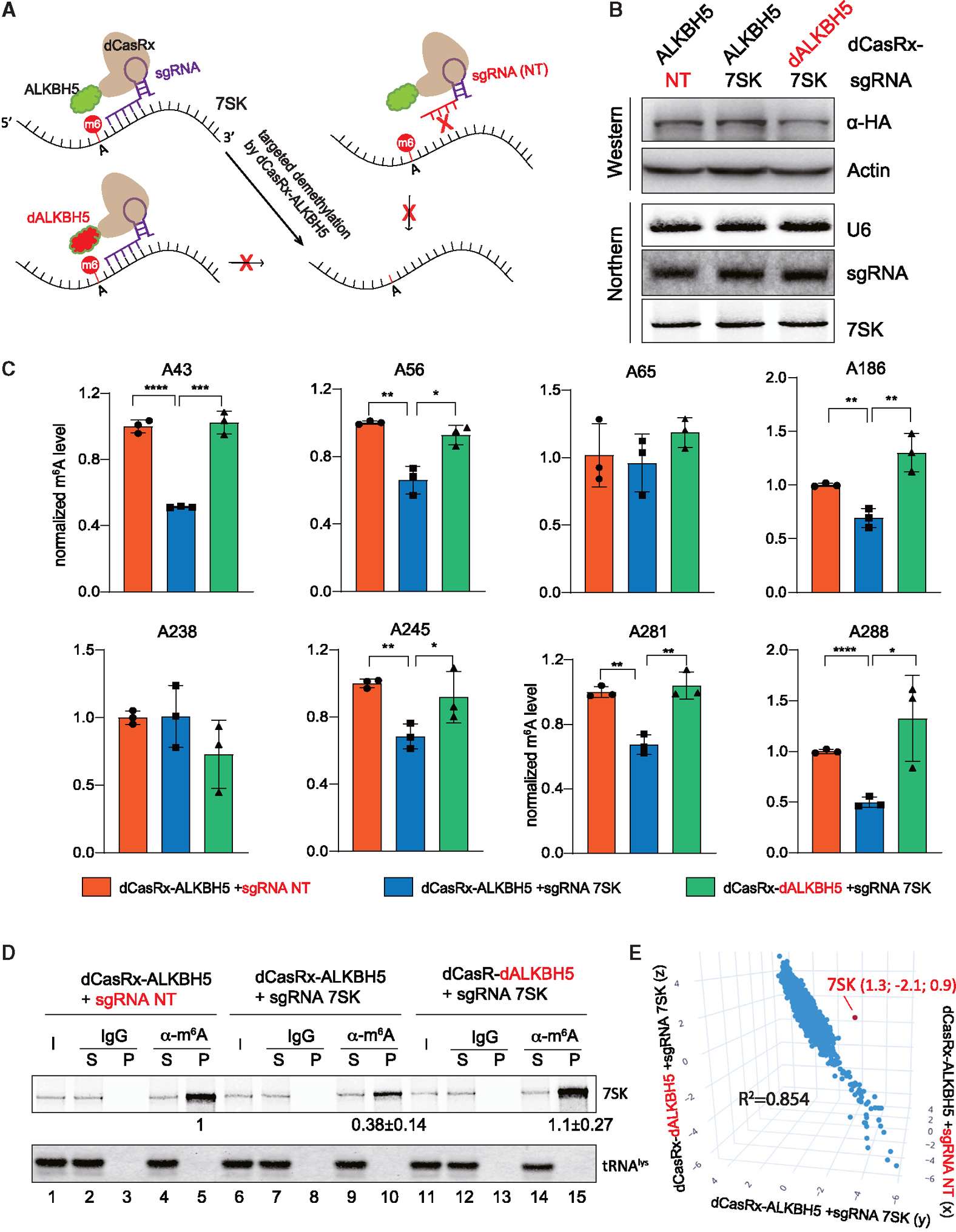
(A) Overview of the fusion dCasRx-ALKBH5 (WT or H204A) proteins for removing m6A modification on 7SK.
(B) Western blot and northern blot detected the dCasRx-ALKBH5 fusion protein expression level and the abundance of sgRNA and 7SK in the 3 engineered A549 cell lines stably expressing fusion dCasRx-ALKBH5.
(C) Normalized m6A levels at A43, A56, A65, A186, A238, A245, A281, and A288 detected by SELECT in 3 A549 cell lines as in (B) (error bars represent SD, t test calculated the p values, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001).
(D) Northern blot analyses of 7SK and tRNAlys after immunoprecipitation using a m6A-specific antibody or IgG control in 3 A549 cell lines as in (B). Input (I) and supernatant (S) are 1.2% of the pellet (P). Quantitation of relative m6A-7SK levels (mean ± SD) in the pellet was derived from 3 independent experiments.
(E) 3D scatter plot of transcriptome-wide relative m6A modifications (log2[m6A-IP/input]) in 3 different A549 cell lines as in (B), detected by triplicate MeRIP-seq experiments. The red dot indicates 7SK. See also Figures S2–S4.
