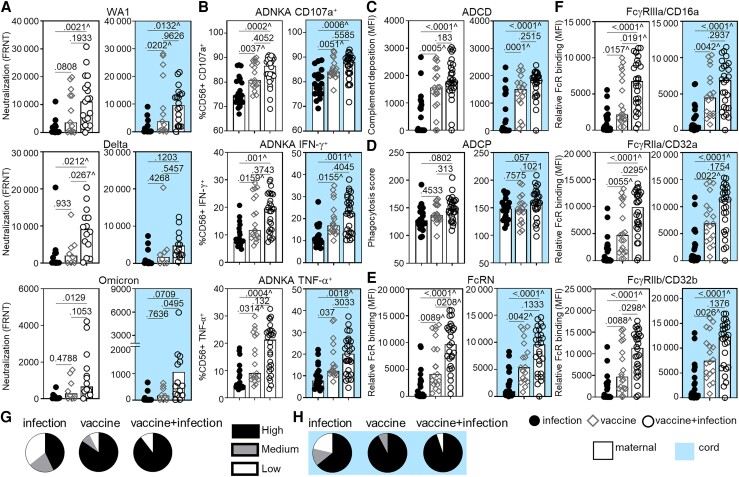
Figure 1.
Increasing maternal and cord blood neutralizing and Fc effector functional magnitude and breadth were observed after infection, vaccination, and vaccination and infection in pregnancy. The bars depict the median of matched maternal (white, left) and cord (blue, right) blood levels of (A) neutralization (FRNT50) against SARS-CoV-2 WA1 (infection n = 14, vaccine n = 13, vaccine + infection n = 19), Delta, and Omicron viruses (infection n = 12, vaccine n = 8, vaccine + infection n = 14); (B) ADNKA by CD107a, IFN-γ, and TNF-α; (C) ADCD; (D) ADCP; and relative binding to (E) FcRN and (F) FcγRIIIa/CD16a, FcγRIIa/CD32a, and FcγRIIb/CD32b specific to receptor-binding domain. B–F, sample sizes are infection n = 20, vaccine n = 18, vaccine + infection n = 27. P values are adjusted for maternal age and body mass index using linear regression. ^ Marks significance after adjustment for multiple comparisons by Benjamini-Hochberg. The proportion of detectable functions was used to categorize individuals as a high, medium, or low responder (Supplementary Figure 4). Polyfunctional breadth is depicted as the percentages of each type of responder within each group in (G) maternal and matched (H) cord samples. Abbreviations: ADCD, antibody-dependent complement deposition; ADCP, antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis; ADNKA, antibody-dependent natural killer cell activation; FRNT50, 50% reduction neutralization test; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α.