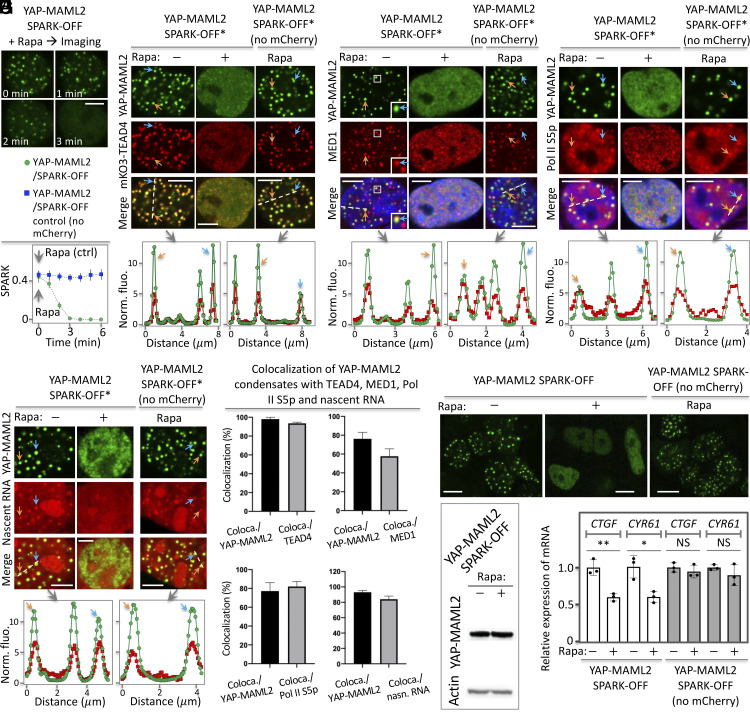
Fig. 6.
The chemogenetic tool SPARK-OFF reveals role of YAP-MAML2 PS on transcription. (A) Rapamycin-activatable SPARK-OFF dissolves YAP-MAML2 condensates. The HEK293 cells expressed FKBP-mEGFP-YAP-MAML2 and NLS-mCherry-Frb. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). (B–E) SPARK-OFF*-driven dissolution of YAP-MAML2 condensates led to condensate dissolution of TEAD4 (B), transcriptional machinery including MED1 (C) and Pol II S5p (D), and nascent RNAs (E). (F) Percentage of YAP-MAML2 condensates that colocalize with puncta of other components. The percentage is determined by the ratio of coloca./YAP-MAML2 = number of colocalized condensates between YAP-MAML2 and TEAD4 divided by number of YAP-MAML2 condensates. Equivalent analysis for other pairs is also shown. Data are mean ± SD (n = 11 cells). (G) Fluorescent images of stable cells expressing SPARK-OFF-tagged YAP-MAML2 or the control. The cells were treated with rapamycin or DMSO, followed by RT-qPCR analysis. No PS: no phase separation. (H) Western blot showing YAP-MAML2 protein abundance level. (I) RT-qPCR analysis of the expression levels of two YAP target genes in cells without and with PS of YAP-MAML2. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). **P-value < 0.01, *P-value < 0.05. NS, not significant. [Scale bars: 5 μm (A–E), 10 μm (G).]