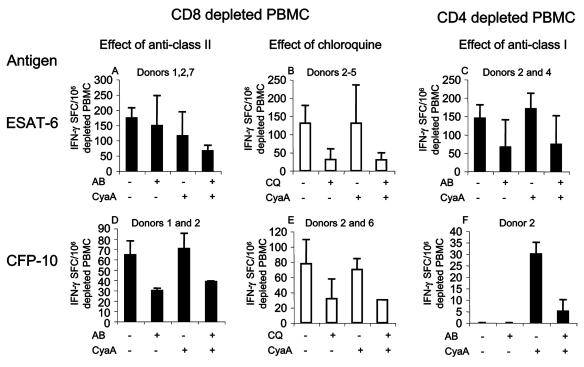
FIG. 4.
Effects of inhibition of antigen presentation on the T-cell responses to free and toxoid antigens. CD8+-depleted (i.e., CD4+-enriched) and CD4+-depleted (CD8+-enriched) PBMC were set up in the overnight IFN-γ ELISPOT in the presence or absence of antibodies to MHC class I and II and isotype control (5 μg/ml) or chloroquine (20 μM). Antigens were added as free ESAT-6 (500 nM) or CFP-10 (250 nM) or as CyaA fusions (50 and 25 nM, respectively). There were insufficient cells to test all combinations in all donors; the donors who were tested and responded are indicated. (A and B) Antibody to HLA-DR moderately inhibited the response to both rESAT-6 and CyaA-ESAT-6 (15 and 43%, respectively). The effect of chloroquine was more marked (77% in both cases). (C) Antibody to MHC class I inhibited the CD8+ T-cell recognition of rESAT-6 and CyaA-ESAT-6 by 56 and 57%, respectively. (D and E) Antibody to MHC class II inhibited the response to both rCFP-10 and CyaA-CFP-10 (53 and 45%, respectively). The effect of chloroquine was again more marked (59 and 57%, respectively). (F) No donor had a CD8+ T-cell response to rCFP-10. In donor 2, antibody to MHC class I strongly inhibited the response to CyaA-CFP-10. Isotype control antibody had no effect on antigen recognition. Values are shown as means ± standard deviation (error bars). IFN-γ SFC, IFN-γ-secreting SFC; AB, antibody; CQ, chloroquine; CyaA, antigen presented as CyaA fusion; +, presence of antibody and/or presentation as CyaA toxoid.