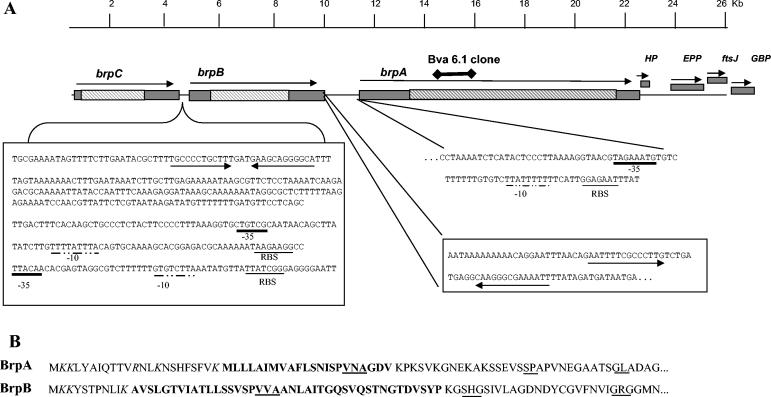
FIG. 3.
Organization of genes on the 26-kb Bva-Brp clone of B. vinsonii subsp. arupensis. (A) brpA, brpB, and brpC coding sequences are represented by rectangular bars, with the arrows showing the direction of transcription. The hatched bars within the coding sequences denote portions of the genes composed of repetitive sequences. Genes downstream of brpA are abbreviated as HP (hypothetical protein), EPP (exopolyphosphatase), ftsJ (cell division protein), and GBP (GTP-binding protein). The 409-bp intervening sequence between the stop codon of brpC and the start codon of brpB is shown. The bidirectional arrows indicate inverted repeats characteristic of transcriptional termination sites for brpC. Two putative brpB promoter sites based on consensus sequences for the ribosome binding site (RBS) (underlined), the −10 site (underlined with a dot-and-dash line), and the −35 site (heavily underlined line) are denoted. The region immediately downstream of the stop codon for brpB is shown with inverted repeats illustrated with the bidirectional arrows. The immediate upstream noncoding region is shown for brpA with putative RBS, −10, and −35 sites. The location of the original truncated Bva-6.1 clone that generated the recombinant protein used in this study is shown above brpA. A scale in kbp is above the diagram. (B) Signal peptides deduced from the amino acid sequences for brpA and brpB. Charged residues are italicized, the hydrophobic central region is in bold, and putative SPase I cleavage sites are underlined. Cleavage sites predicted by the SignalP program follow the underlined VNA and VVA of BrpA and BrpB, respectively.