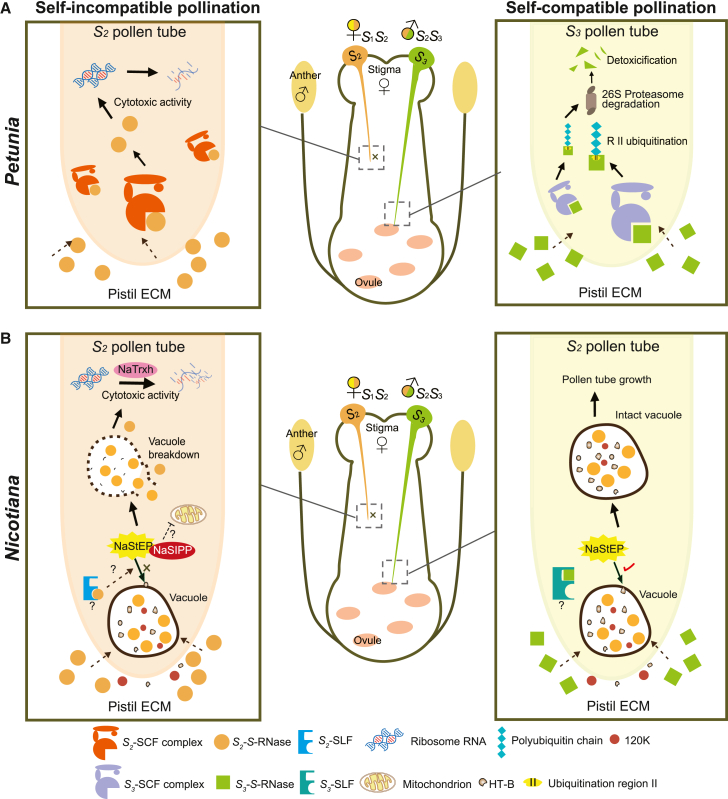
Figure 2.
Two S-RNase-based SI models.
(A) The collaborative degradation model in Petunia. In compatible pollen tubes, SLF forms an SCF (Skp1/Cullin1/F-box) complex that polyubiquitinates all nonself S-RNase proteins, with PhS3-RNase R II as the main ubiquitination region. The polyubiquitinated S-RNases are further degraded by the 26S proteasome, enabling the growth of compatible pollen tubes. Conversely, in incompatible pollen tubes, the interaction between self S-RNase and SLF fails to produce a functional SCF complex; self S-RNase thus evading degradation and acting as a cytotoxin to inhibit pollen tube growth.
(B) The compartmentalization model in Nicotiana. Nonself S-RNases, along with HT-B and 120K, become sequestered within an intact vacuole upon uptake by the compatible pollen tube, preventing the cytotoxic activities of S-RNase. HT-B acts as a key molecule in the S-RNase-containing vacuole, as it is degraded in incompatible pollen tubes. The stability of HT-B relies on the presence of NaStEP, which protects HT-B from degradation by its proteinase inhibitor activity. NaStEP also interacts with NaSIPP, potentially leading to mitochondrial destabilization and eventual cell death. The recognition event between SLF and self S-RNase triggers specific interactions among these modifier genes, resulting in breakdown of the vacuole and disruption of self S-RNase compartmentalization. Once free S-RNases are in the cytosol, their ribonuclease activity is further enhanced by NaTrxh.