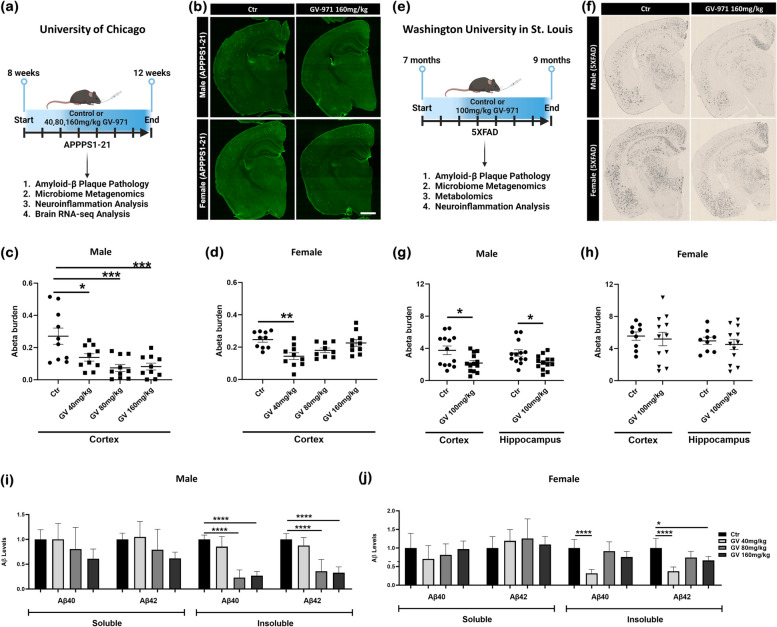
Fig. 1.
GV-971 reduces amyloidosis in a dose and sex-dependent manner. a University of Chicago experimental design. b Representative images of brains stained with anti-Aβ antibody 3D6 depicting the effect of GV-971 on Aβ plaque burden in APPPS1-21 mice. c Quantification of % area covered by 3D6+ Aβ plaques in cortices of APPPS1-21 male mice (n = 10). d Quantification of % area covered by 3D6+ Aβ plaques in cortices of APPPS1-21 female mice (n = 9–11). e Washington University in St. Louis experimental design. f Representative images of brains stained with anti-Aβ antibody HJ3.4 showing the effect of GV-971 on Aβ plaque burden in 5XFAD mice. g Quantification of % area covered by HJ3.4+ Aβ plaques in cortices of 5XFAD male mice (n = 13). h Quantification of % area covered by HJ3.4+ Aβ plaques in cortices of 5XFAD female male (n = 9–12). i Quantification of insoluble and soluble Aβ 40 and 42 isoforms extracted from cortical tissue of male APPPS1-21 mice (n = 10). j Quantification of insoluble and soluble Aβ 40 and 42 isoforms extracted from cortical tissue of female APPPS1-21 mice (n = 9–11). Data presented as SEM. Significance determined using a One-way ANOVA test followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison post hoc test (c, d, i, j), and unpaired t-test (g, h). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001