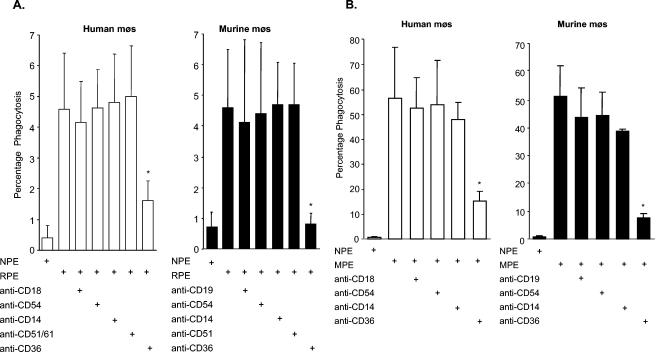
FIG. 1.
Anti-CD36 antibody reduces phagocytosis of RPEs by human and murine macrophages (mφs). Human monocyte-derived macrophages and murine macrophages were cotreated with IgG Fc fragments (20 μg/ml) to block Fc receptors and 10 μg of MAbs to human or murine macrophage receptors per ml (where indicated), followed by incubation with non-PEs (NPE) or RPEs (A) and MPEs (B) (12, 15). Phagocytosis was assessed by light microscopy by counting 500 to 1,000 cells and expressed as the percentage of macrophages that had phagocytosed at least one RPE. The results show that Fc receptor-blocked human and murine macrophages can internalize RPEs. CD36 receptor blockade with 10 μg of anti-CD36 MAb per ml resulted in a significant decrease in phagocytosis of nonopsonized RPEs by human macrophages (mean decrease of 65%, left side) and murine macrophages (mean decrease of 82%, right side). MAbs to ICAM-1 (CD54), CD18 or CD19 (isotype controls), integrins (CD51/61, CD51), and CD14 did not result in a significant decrease in phagocytosis. Experiments were performed in triplicate, and the data shown represent the mean ± the standard deviation of at least six independent experiments. (*, P < 0.05 for RPE versus anti-CD36; Student's t test).