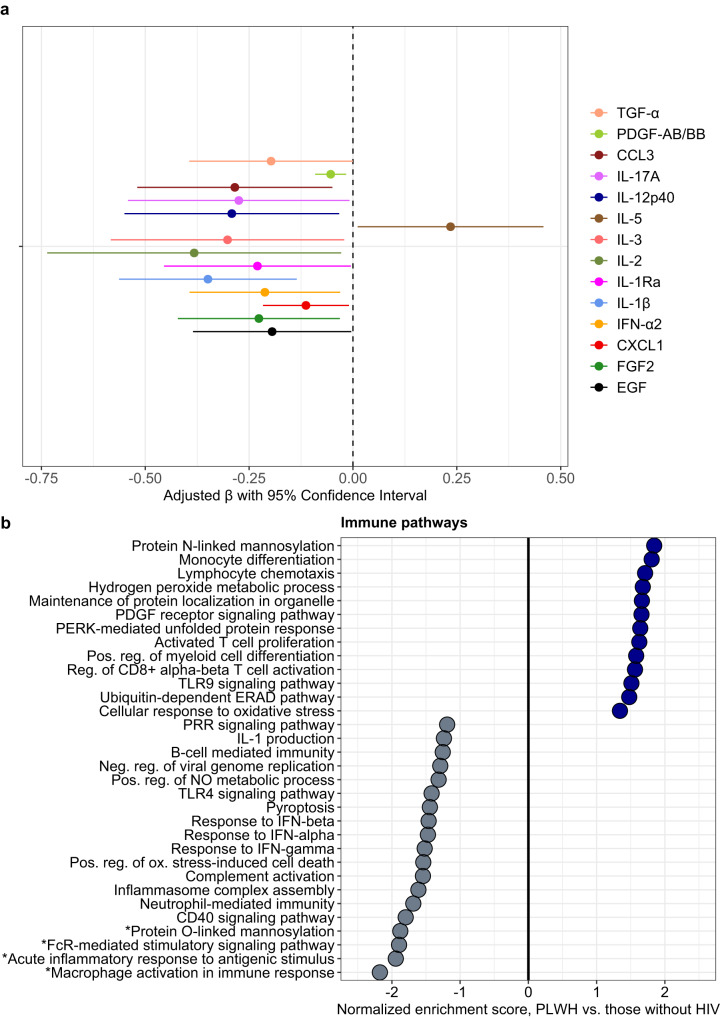
Fig. 6. Immune mediators and biological pathway enrichment in SARS-CoV-2/HIV co-infection.
a Associations between HIV co-infection and log10-immune mediator concentrations in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection (N = 302; persons living with HIV, N = 33; patients living without HIV, N = 269; 4 patients without definitive assessment of HIV co-infection excluded); coefficients with 95% confidence interval bars generated in multivariable linear regression models including log10-transformed mediator concentration as dependent variable and HIV co-infection (binary), age (continuous), self-reported sex (binary), and WHO clinical severity classification (categorical) as independent variables. b Differential enrichment of key biological pathways among patients living with HIV (N = 16) vs. those without HIV (N = 82; 2 patients without definitive assessment of HIV co-infection excluded); pathway enrichment determined using Gene Set Enrichment Analysis applied to differentially expressed gene sets generated in a DESeq2 model of whole-blood RNAseq data adjusted for age (continuous), self-reported sex (binary), and WHO clinical severity classification (categorical). *Differentially enriched pathways at FDR q value ≤ 0.10; remainder of pathways associated with FDR q value > 0.10. PRR pathogen recognition receptor, NO nitric oxide, ERAD Endoplasmic-reticulum-associated protein degradation. Source data are provided in the Source Data file.