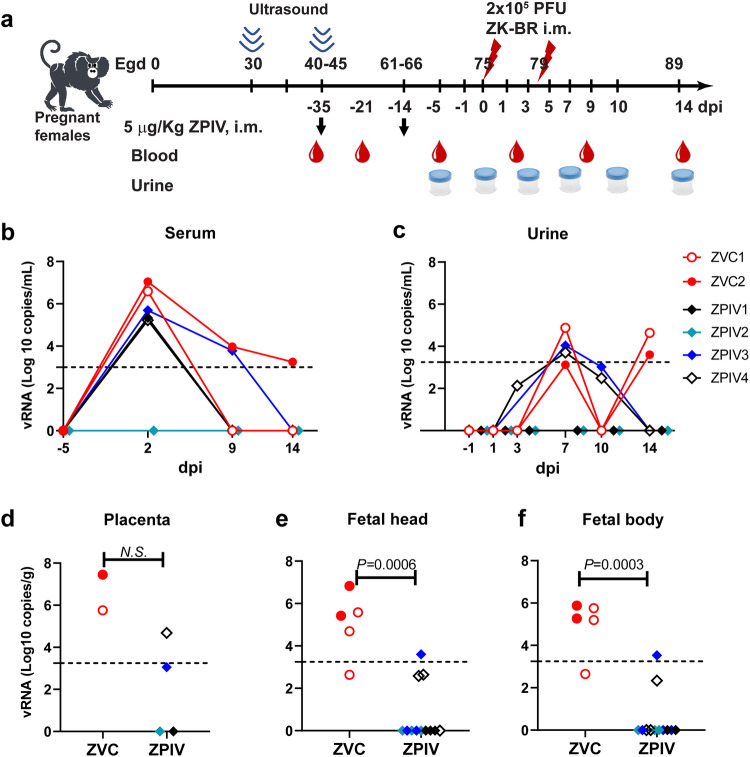
Fig. 1. Protection by ZPIV vaccination during pregnancy in marmosets.
Pregnant females (n = 4) received intramuscular injections of 2.5 μg alum adjuvanted ZPIV at egd 40 and 61. Then, 2 weeks after the boost, the marmosets received i.m. injections of 2.5 × 105 PFU of ZIKV twice at egd 75 and 79. As controls, unvaccinated pregnant marmosets (n = 2, ZVC) were included and infected with the virus at comparable gestational days (egd 75 and 79) of pregnancy (a). All marmosets were bled at 0, 2, and 5- weeks post-prime vaccination as well as −5, 2, 9, and 14 dpi. Urine samples were prepared at −1, 1, 3, 7, 10 and 14 dpi. At 14 dpi (egd 89), dams were sacrificed, and the placentas and fetuses were extracted. Viral genomic RNA levels were quantitated using Real-Time RT-qPCR in total RNA prepared from serum (b), urine (c) at indicated time, placental tissues (d) at three locations per marmoset, a half of fetal head (e) and a half of fetal body (f). Dotted line indicates the limit of quantitation (Ct value < 35). Data were analyzed using the Mann–Whitney test to detect significant differences between groups. The ANOVA test was used to determine significant differences between group and time.