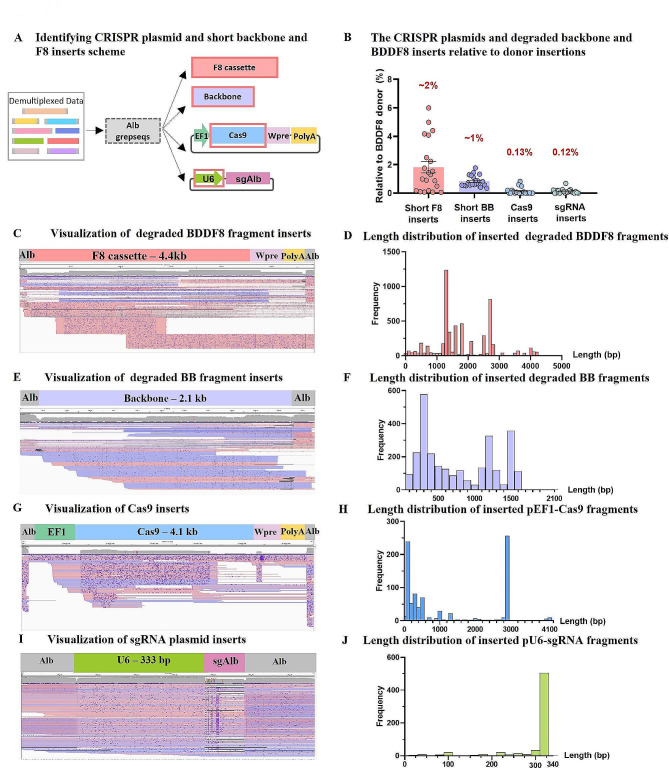
Fig. 7.
Characterization of CRISPR plasmid, short plasmid backbone, and F8 sequence insertions at the edited Alb site. (A) Strategy to analyze short insertions post-editing: The analysis began with grepseqs derived from regions 146 bp left and 186 bp right of the Alb cleavage site. Reads with insertions other than the F8 donor were isolated using unique sequences from Cas9 and U6, excluding full-length backbone and F8 insertions. Short plasmid backbone (defined as < 1700 bp) and F8 sequences (< 4400 bp) were then analyzed. (B) Insertion comparison: The frequency of reads with inserted short F8, short backbone, and CRISPR plasmids was compared to those carrying double-cut donor sequences. Error bars represent mean ± SEM, based on data from 21 mice. Paired two-sided Student’s t-tests were used. (C) Short F8 inserts visualization: 200 randomly selected short F8 inserts are visualized against the reference sequence of Alb gDNA flanking the entire F8 cassette sequence. (D) Short F8 inserts length distribution. (E) Short backbone inserts visualization: 200 randomly selected short backbone inserts are visualized against the reference sequence of Alb gDNA flanking the entire plasmid backbone sequence. (F) Short backbone inserts length distribution. (G) Cas9 Plasmid insertions visualization: Visualization against the reference sequence of Alb gDNA flanking the CRISPR plasmid sequence, excluding the backbone. (H) Cas9 sequence inserts length distribution analysis. (I) Visualization of inserted sgRNA plasmid fragments. (J) Length distribution of sgRNA plasmid sequence Inserts