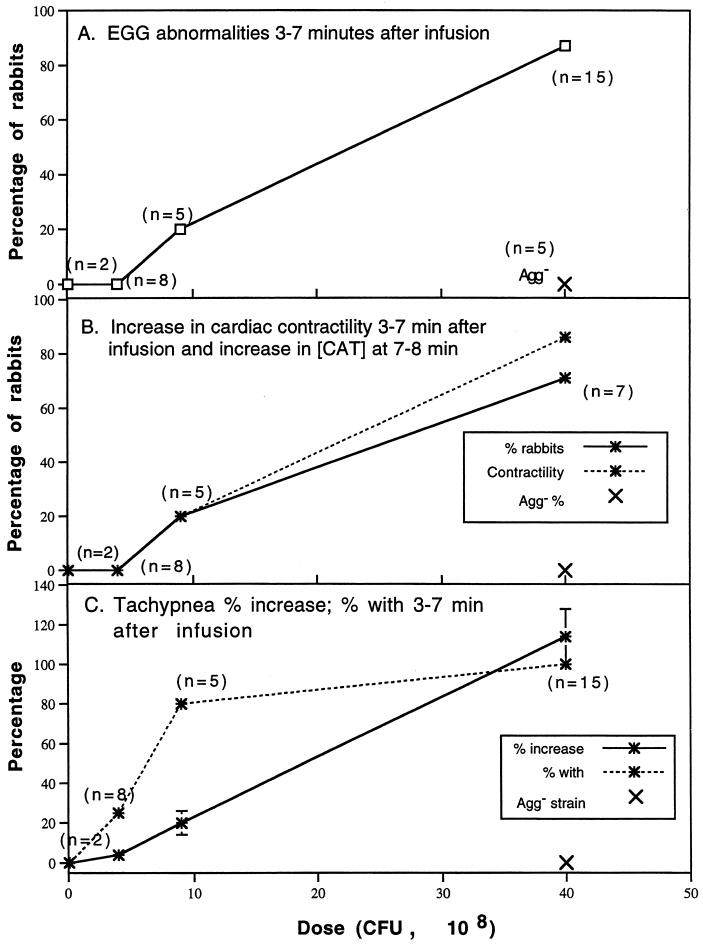
FIG. 4.
Cardiopulmonary consequences of S. sanguis bacteremia. For selected variables, the Agg+ dose-dependent changes in frequency or magnitude are presented. Two rabbits infused with 0.1 × 108 CFU of the Agg+ strain and five with 40 × 108 CFU of the Agg− strain are also included for comparison. Note that the Agg− strain had no effect upon any of the cardiopulmonary variables studied. The regression line for each variable shown was significantly different from zero (linear regression analysis). (A) ECG abnormalities at t = 3 to 7 min. During this period after infusion, the ECG was monitored and changes were evaluated for the numbers of rabbits shown. (B) Increases in cardiac contractility (t = 3 to 7 min) and catacholamine concentration (t = 7 to 8 min). Cardiac contractility was computed as dP/dt as described in Materials and Methods. In the same rabbits, catacholamine concentrations were determined by radioenzymatic assay as described in Materials and Methods. (C) Frequency and percent increase in tachypnea at t = 3 to 7 min. Note the high frequency but comparatively low magnitude with an Agg+ dose of 9 × 108 CFU. Catecholamines did not vary from baseline in rabbits given Agg+ doses of 0.1 and 4 × 108 CFU. Since the cardiopulmonary responses were similar to rabbits given lower doses of the Agg+ strain, rabbits given 40 × 108 CFU of the Agg− strain were not sampled for catecholamines.