Figure 3.
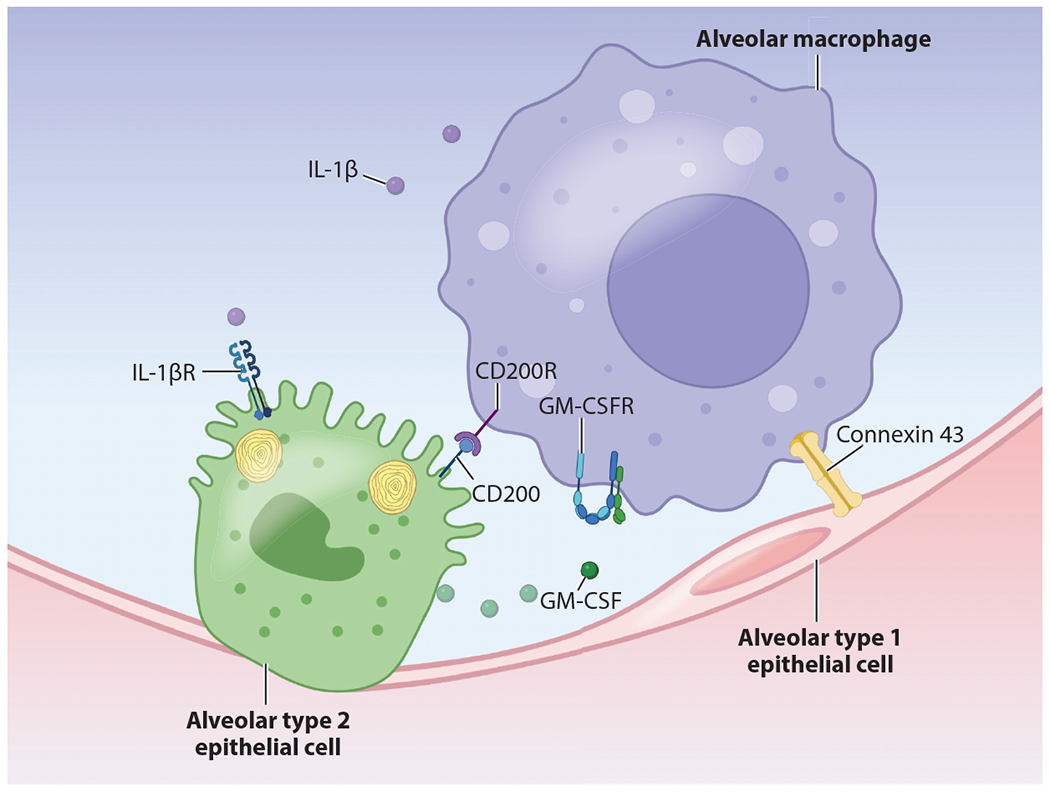
Immune signaling in the alveolus. At homeostasis, the alveolus is maintained in a quiescent state via bidirectional signaling between the alveolar epithelium and alveolar macrophages. These mechanisms include production of soluble factors such as IL-1, which is secreted by myeloid immune cells and promotes AT2 cell proliferation via the IL-1 receptor. GM-CSF is secreted by AT2 cells and signals via PPAR-γ to induce a transcriptional program that promotes surfactant homeostasis. AT2s also express the cell surface ligand CD200, which provides immunoregulatory signals to alveolar macrophages via CD200R. Several recent studies have also shown coordinated calcium-mediated signaling via gap junctions (notably connexin 43). Abbreviations: AT2, alveolar type 2; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IL, interleukin; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor. Figure adapted from images created with BioRender.
