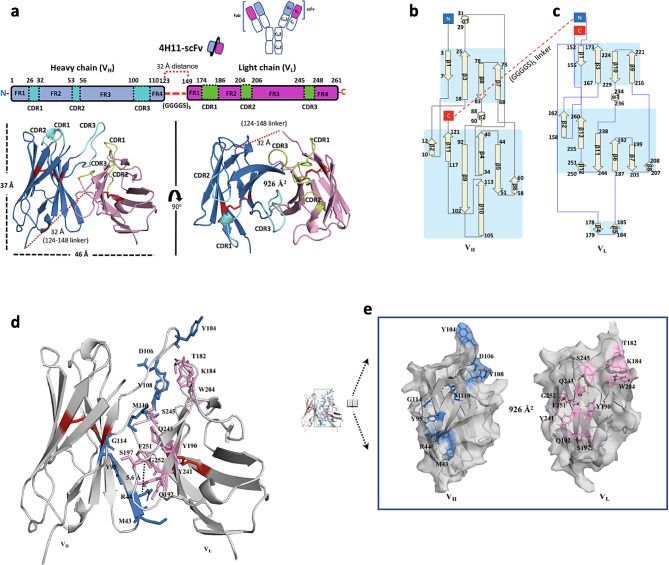
Fig. 4.
Overall structure of 4H11-scFv and interaction between VH and VL. (a) Schematic diagram showing the domain structures of Heavy chain (Hc: 1-123) and Light chain (Lc: 149–261), as well as the positions of 3 CDRs (residue positions: 26–32, 53–56, 100–110) at VH (cyan) and 3 CDRs (residue positions: 174–186, 204–206, 245–248) at VL (forest) interacting with MUC16ecto. CDR: complementary determining region. The shortest distance from C-terminal of VH to N-terminal of VL, the flexible linker (GGGGS)5 lengths (red dots) with no electron density map (residues 124–148), was 32 Å which corresponds to at least 13 amino acid-lengths. Each domain has one S-S bridge (red) (C22 – C96 at VH and C171 – C242 at VL) for stable folding. The solvent-accessible area of the interface between VH-VL was 926 Å2. (b, c) Secondary structure topology diagram of VH (left panel) or VL (right panel) of 4H11-scFv, the eleven sheets and two short helices for VH and the thirteen sheets and one helix for VL are represented. C-terminal (red) of VH is connected to N-terminal (blue) of VL via (GGGGS)5 linker (red dots). (d) Interacting residues at interface regions between VH and VL are colored as blue (VH residues) and pink (VL residues). The cationic sidechain of R44 (VH) form a favorable cation- π pair (black dot; 5.6 Å distance) with an aromatic sidechain of F251 (VL) to improve overall stability. (e) An open-book view of the interface with interacting residues. See Table S2 for detailed interacted residues