Fig. 3 |. Interface 7 of the OPA1 assembly is essential for the regulation of mitochondrial morphology.
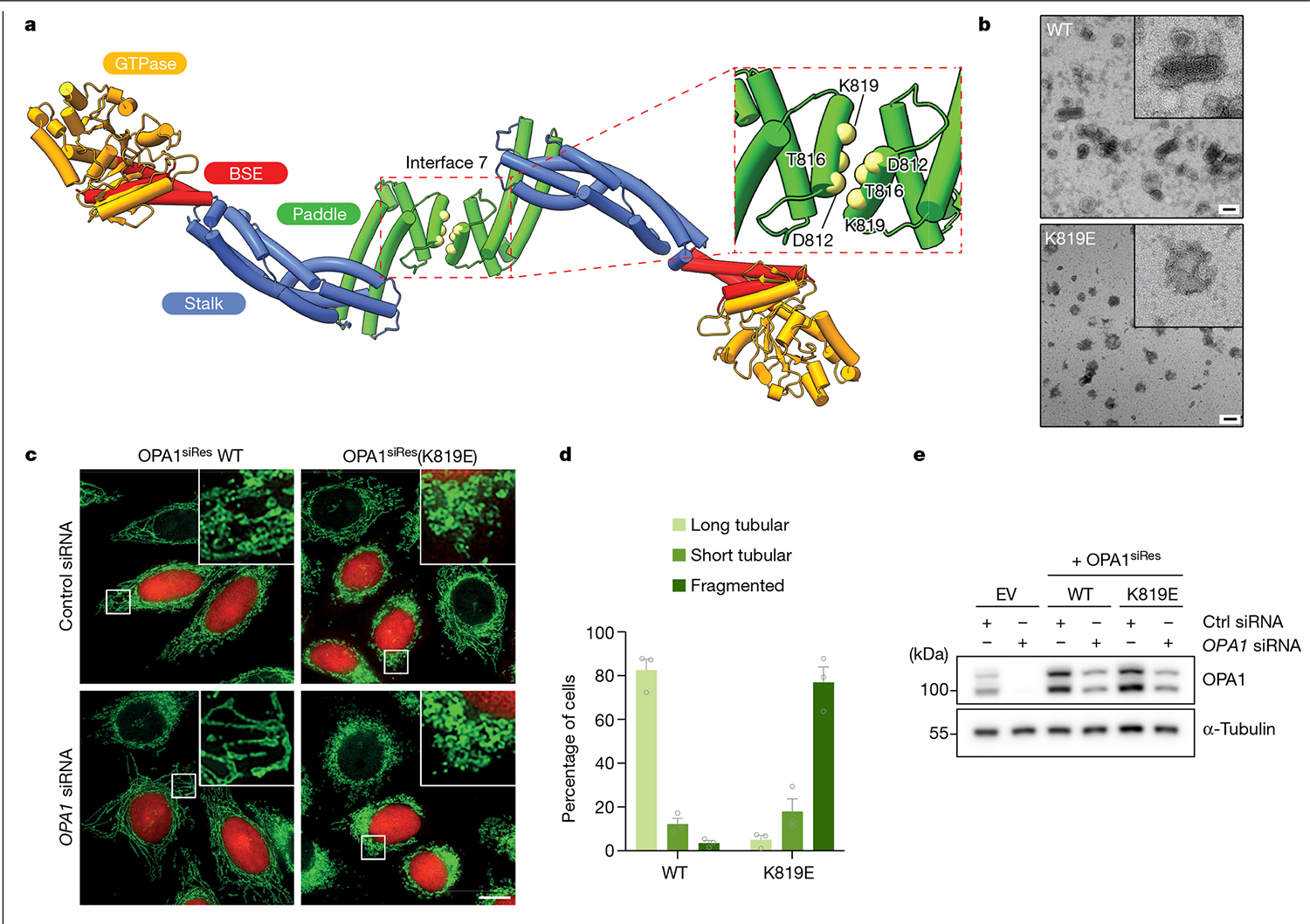
a, Top view of the structural model of the membrane-bound S-OPA1, revealing the dimerization of PDs. Top right, magnified view of the area indicated by the dashed box showing interface 7 between two PDs. α3P helix residues involved in interface 7 formation are shown as solid spheres (yellow) and numbered. b, Negative-stain TEM analyses of WT OPA1 and the OPA1(K819E) mutant in the presence of CL-enriched liposomes. Negative-stain electron micrographs show impaired liposome binding and remodelling activity of the OPA1(K819E) mutant compared with the WT. Inset, magnified views of selected liposomes. Scale bars, 100 nm. c, Fluorescence microscopy images of WT and interface-7-mutant OPA1(K819E) in mitochondrial morphology analyses. HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated siRNA-resistant OPA1 constructs and then subjected to RNA interference using the indicated siRNAs. The mitochondrial network was visualized by staining for the outer membrane protein TOMM22 (green), and co-transfected mCherry-NLS (red) was used to identify transfected cells. The experiment was performed in biological triplicate. Scale bar, 20 μm. d, Quantification of microscopy images of OPA1 WT and the K819E mutant. Mitochondrial phenotypes observed in HeLa cells transiently expressing human OPA1 variants as described in c. The average percentage of cells belonging to each of three morphological classifications across three experimental replicates. n = 238 cells expressing WT OPA1 over three experimental replicates and n = 283 cells expressing OPA1(K819E) over three experimental replicates. Data are the mean ± s.e.m. percentage of cells across three experimental replicates. e, Expression and stability of the siRNA-resistant OPA1 proteins were assessed by immunoblot analysis of lysates derived from HeLa cells transfected with either empty vector or the indicated siRNA-resistant OPA1 constructs before treatment with the indicated siRNAs. n = 3 independent experiments.
