Extended Data Fig. 1 |. Purification and functional characterization of the human S-OPA1 construct.
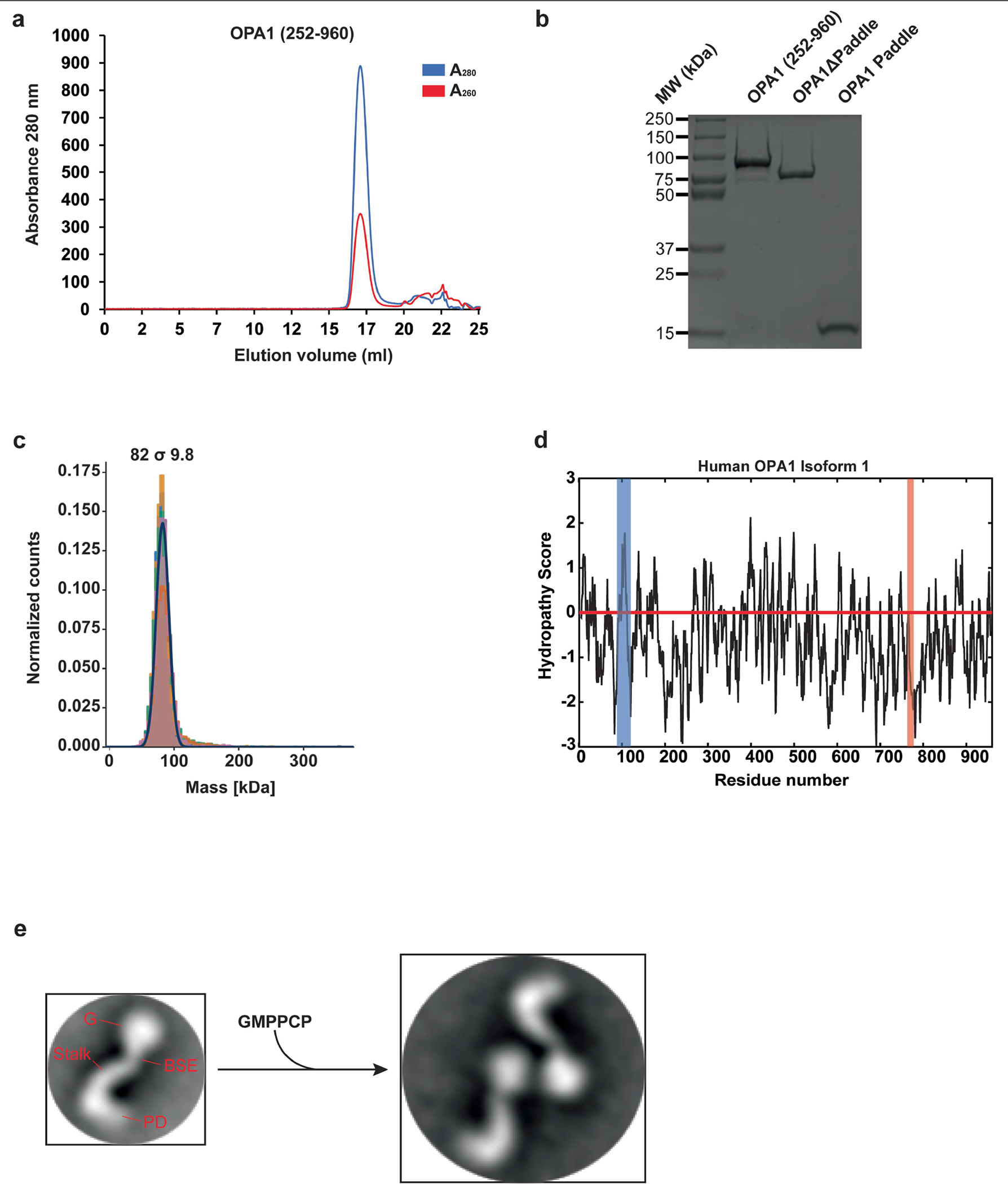
Using a recombinant Escherichia coli expression system, we expressed and purified human S-OPA1 (residues 252–960) in the presence of detergents by Ni2+-affinity and gel filtration chromatography. a, A representative size exclusion chromatogram of the human S-OPA1. b, Purified S-OPA1 constructs on an SDS-PAGE gel stained with Coomassie blue. Performed in technical triplicate. c, Mass photometry profile of nucleotide-free human S-OPA1 reveals an apparent molecular mass of 82 σ 9.8 kDa, which corresponds to a monomeric state. d, Kyte and Doolittle hydropathy plot of full-length human OPA1 isoform 1. Hydrophobic regions corresponding to the transmembrane (TM) region and fusion loop are highlighted in blue and red, respectively. The red line indicates the zero baseline on the hydropathy scale. e, To assess the proper folding and nucleotide-dependent dimerization of recombinant S-OPA1, we incubated the sample with the non-hydrolysable analogue GMPPCP, Mg2+, and K+. Then, using negative-stain transmission electron microscopy (TEM), we observed that S-OPA1 forms dimers via GTPase domain interactions. Representative negative-stain EM 2D class averages of human S-OPA1 from the negative-stain data collected on Tecnai T12 microscope equipped with CCD camera showing that particles have well-defined shapes with modular domain architecture. Monomeric human S-OPA1 forms G domain dimers in the presence of non-hydrolysable GTP analogue GMPPCP.
