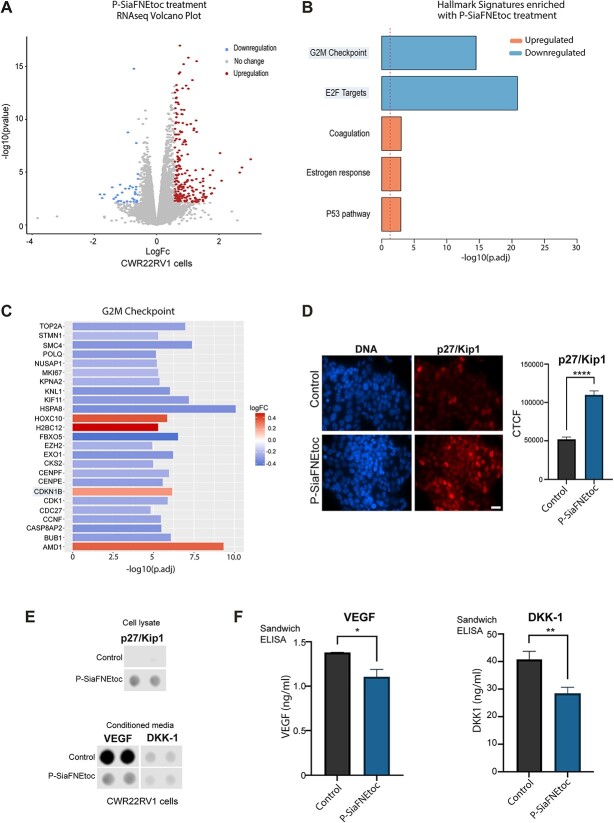
Fig. 5.
Inhibition of sialylation in prostate cancer cells using P-SiaFNEtoc regulates oncogenic proteins important in prostate tumor progression. A) Volcano plot of RNA-seq data to show 254 genes that are differentially expressed in CWR22RV1 cells in response to treatment with 2 μM P-SiaFNEtoc for 72 h (log2FC > |0.58| + adjusted P-value < 0.05). B) Ensemble gene set enrichment analysis of genes regulated by P-SiaFNEtoc treatment reveals downregulation in the “G2M checkpoint” and “E2F targets” hallmark signatures. C) Heatmap to illustrate the top 25 genes with roles in the G2M checkpoint that are significantly differentially expressed in cells treated with P-SiaFNEtoc. D) Validation at the protein level using immunocytochemistry shows p27/Kip1 (which is encoded by the CDKN1B gene) is significantly upregulated in CWR22RV1 treated with P-SiaFNEtoc. Scale bar is 20 μm. E) Analysis of CWR22RV1 cells using a proteome profiler oncology Array identified an increase in p27/Kip1 levels in cell lysate samples and a decrease in VEGF and DKK-1 levels in conditioned media samples from cells treated with P-SiaFNEtoc. F) Sandwich ELISA assays confirm significant downregulation of DKK-1 and VEGF in conditioned media samples from P-SiaFNEtoc treated CWR22RV1 cells.