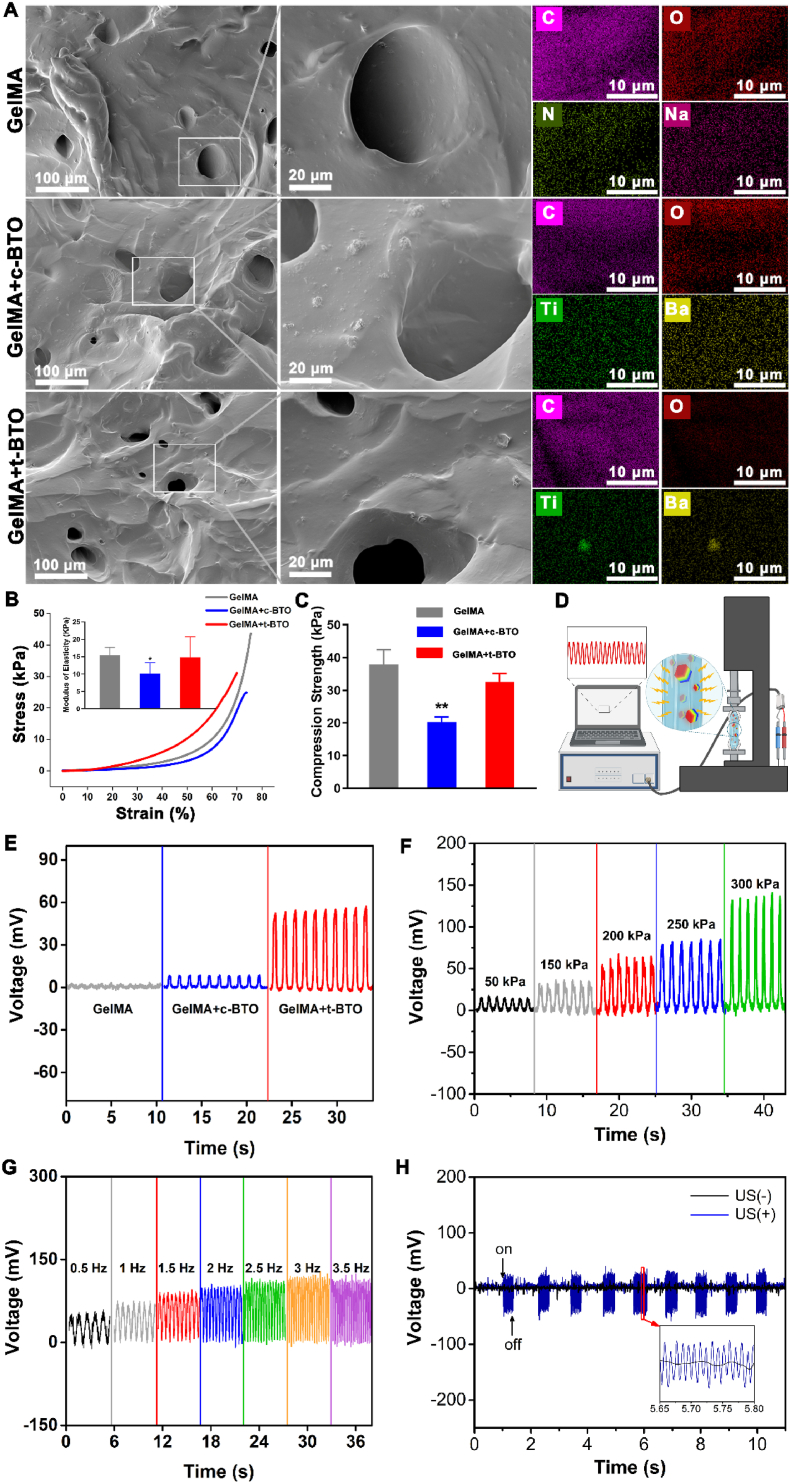
Fig. 2.
Characterization of piezoelectric properties of piezoelectric hydrogels. (A) SEM images and EDX surface-scan element distribution of GelMA, GelMA + c-BTO, and GelMA + t-BTO. (B) Compressive stress-strain curves (the inserted picture represents elastic modulus) and (C) compression strength of GelMA, GelMA + c-BTO, and GelMA + t-BTO. (D) Schematic diagram of the piezoelectric performance test system for the piezoelectric hydrogels. (E) Open-circuit voltages of generator devices made from various hydrogels under a force of 200 kPa. (F) Open-circuit voltages of devices made from GelMA + t-BTO hydrogel under variable forces from 50 to 300 kPa. (G) Open-circuit voltages of device made from GelMA + t-BTO hydrogel under constant force within the frequency range of 0.5–3.5 Hz. (H) Mechanical-electric response of GelMA + t-BTO hydrogel before and after ultrasound stimulation.