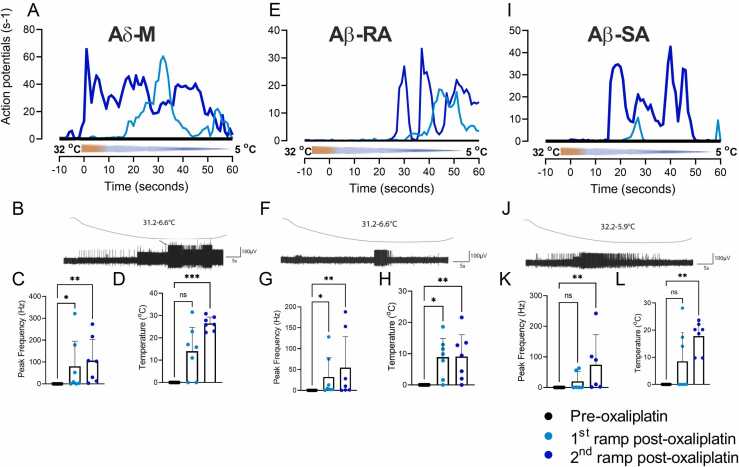
Figure 5.
Aberrant cold sensitivity of oxaliplatin-treated AβSA, AβRA, and AM fibers. Application of oxaliplatin to receptive fields of A fibers conferred aberrant sensitivity to stimulation with a cooling ramp (from 32 °C to less than 10 °C, during 60 seconds). None of the A-fibers represented here responded to cold before oxaliplatin treatment. (A, E, I) Lines represent average firing frequencies for each A fiber type. Light blue lines are responses to the first cold ramp after oxaliplatin treatment, dark blue line represents responses to second cold ramp posttreatment. Typical responses evoked by cooling in AM (B), AβRA (F), and AβSA (J) fibers are shown together with the respective peak firing frequencies (C, G, K) and temperature response thresholds (D, H, L). The second cold ramp generated cold-evoked activity at warmer temperatures than the first ramp in AM and AβSA units (both P < .05, Wilcoxon matched-pair signed rank test, n = 7). Abbreviation: AβSA, Aβ slowly adapting fiber.