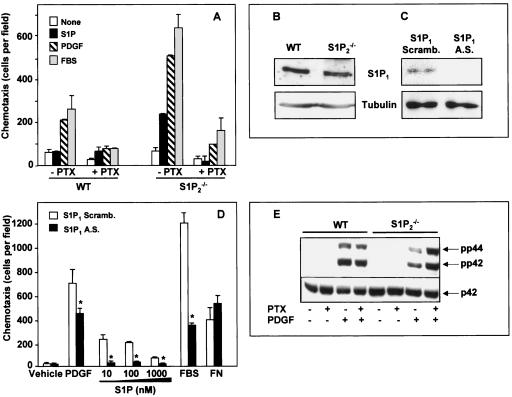
FIG. 4.
Involvement of S1P1 in PDGF-induced chemotaxis. (A) Wild-type (WT) and S1P2−/− MEFs were cultured in serum-free medium for 12 h in the absence or presence of PTX (200 ng/ml). Cells were allowed to migrate for 4 h toward vehicle, S1P (10 nM), PDGF (20 ng/ml), or FBS (20%), and chemotaxis was measured. (B) Expression of S1P1 receptor in wild-type and S1P2−/− MEFs was determined by Western blotting with an antibody against S1P1. The membranes were stripped and reprobed with an antibody against tubulin to show equal loading. (C and D) S1P2−/− cells were transfected with either scrambled (Scramb.; open bars) or antisense (A.S., filled bars) oligonucleotides against S1P1 receptor and (C) analyzed for the expression of S1P1 receptor by Western blotting. Tubulin expression was used as a loading control. (D) Duplicate cultures were serum starved for 12 h and then allowed to migrate toward PDGF (20 ng/ml), serum (20%), or the indicated concentrations of S1P or fibronectin (20 μg/ml). Similar results were obtained in two additional experiments. *, P < 0.05. (E) Wild-type and S1P2−/− MEFs were serum starved overnight in the absence or presence of PTX (100 ng/ml) and then stimulated without or with PDGF (20 ng/ml) for 5 min as indicated. Equal amounts of cell lysate proteins were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-phospho p42/44 antibodies. Blots were stripped and reprobed with anti-ERK2 as a loading control.