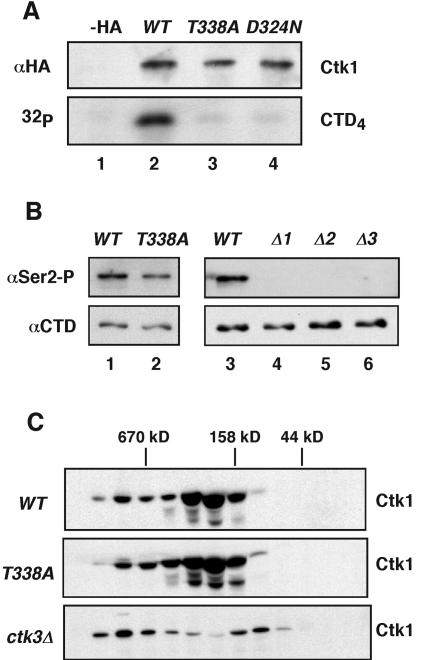
FIG. 2.
Thr-338 phosphorylation is required for Ctk1 activity. (A) Ctk1-HA was immunoprecipitated from yeast strains expressing vector (−HA), wild-type (WT) Ctk1, Ctk1T338A, and Ctk1D324A (lanes 1 to 4). The expression levels and efficiencies of immunoprecipitation were verified by immunoblotting with rabbit anti-HA antibodies (top). Immunoprecipitated Ctk1 complexes were assayed for their CTD kinase activity using a CTD4 peptide as the substrate in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP (bottom). The reaction products were resolved by SDS-PAGE and visualized by autoradiography. (B) Yeast strains corresponding to CTK1, ctk1T338A (lanes 1 and 2) and the wild type and ctk1Δ, ctk2Δ, and ctk3Δ mutants (lanes 3 to 6) were examined for their levels of RNA pol II phosphorylation. Proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted for the presence of phosphorylated serine 2 (Ser2-P) using H5 antibodies; unphosphorylated RNA pol II was detected using 8WG16 antibodies (bottom). (C) Yeast extracts from CTK1, ctk1T338A, and ctk3Δ strains were fractionated on a Sephadex-200 gel filtration column and resolved by SDS-PAGE. The distribution of Ctk1-HA among the fractions was determined by immunoblotting with rabbit anti-HA antibodies. The positions of molecular weight markers are indicated at the top.