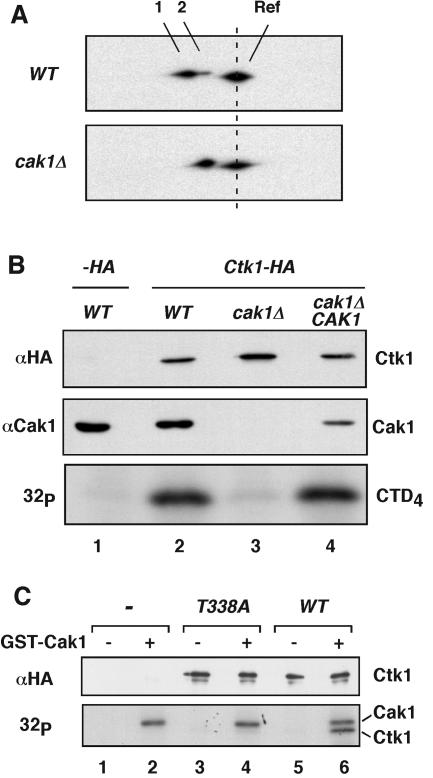
FIG. 3.
Cak1p phosphorylates Ctk1 on Thr-338. (A) Ctk1-8DE-HA was expressed in wild-type (WT) and cak1Δ cells and resolved on two-dimensional gels as described in the legend to Fig. 1C. Spots 1 and 2 correspond to phosphorylated and unphosphorylated forms of Ctk1-8DE-HA, respectively. Ctk1-HA was included as a reference (Ref) protein. (B) Yeast extracts were prepared from wild-type, cak1Δ, and cak1Δ/CAK1 cells also containing an empty plasmid (−HA, lane 1) or a plasmid expressing Ctk1-HA (lanes 2 to 4). The presence of Cak1p was determined by immunoblotting with an anti-Cak1p monoclonal antibody (middle). Ctk1-HA-containing complexes were immunoprecipitated. The level of precipitated Ctk1-HA was determined by immunoblotting using rabbit anti-HA antibodies (top). The immunoprecipitated Ctk1 was also used to phosphorylate CTD4 in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP (bottom). (C) Coupled transcription/translation reactions were programmed with an empty vector (−), ctk1T338A-HA, and CTK1-HA. The expressed proteins were immunoprecipitated with 12CA5 antibodies and incubated with [γ-32P]ATP in the absence (lanes 1, 3, and 5) or presence (lanes 2, 4, and 6) of recombinant GST-Cak1p (bottom). The abundance of synthesized Ctk1-HA was verified by immunoblotting with rabbit anti-HA antibodies (top). Note that we used GST-Cak1p in this experiment, which has a molecular mass of 67 kDa and runs close to Ctk1-HA (63 kDa).