Figure 6. Model for Abl2 in regulating MT dynamics.
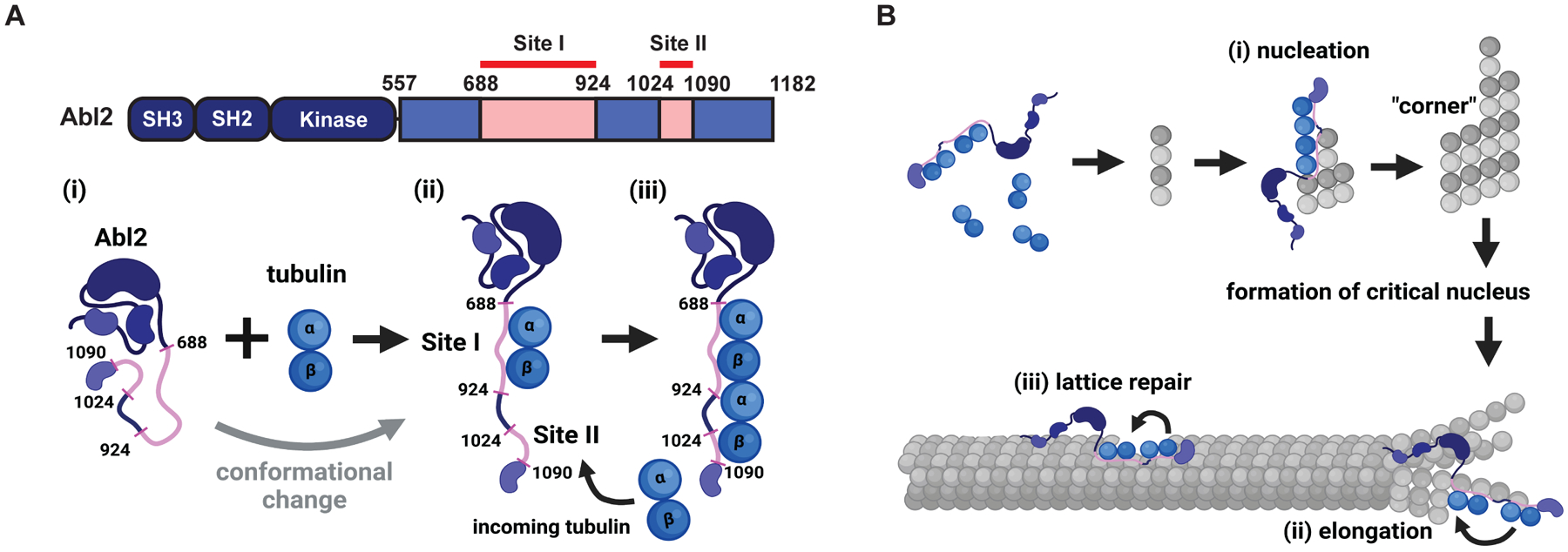
(A) Schematic of full length Abl2 regulating MT growth, nucleation, and lattice repair. (i) Abl2 forms a conformational change when it binds a tubulin dimer. (ii) Abl2 directly interacts with tubulin dimers using its solvent-exposed 688–924 (site I). The 1024–1090 region (site II) is less accessible in the native conformation. (iii) Binding to a single tubulin dimer via site I may induce a conformational change within 557-C, leading to solvent exposure of site II, which can further recruit an additional dimer. (B) Abl2 can dock onto: (i) tubulin oligomers to facilitate the incorporation of new tubulin dimers for nucleation; (ii) on growing MT ends to promote elongation; and (iii) on regions along MTs that harbor lattice defects to promote rescue and repair.
