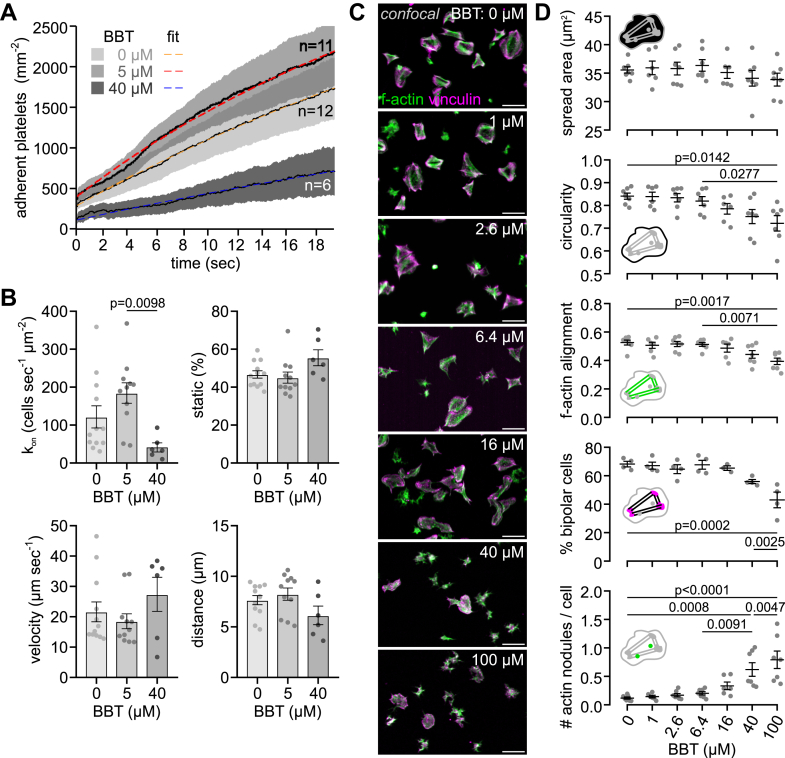
Figure 3.
Partial myosin IIA inhibition preserves mechanotransduction by primary adhesion receptors. (A) Effect of para-amino blebbistatin (BBT) on glycoprotein Ib-mediated adhesion of platelets to von Willebrand factor (VWF) under arterial shear (1500 s−1). Whole blood was preincubated with vehicle, 5 or 40 μM para-amino BBT, and 3,3′-dihexyloxacarbocyanine iodide (DiOC6) for 5 minutes at 37 °C and then perfused through flow channels with VWF-coated glass bottoms. Movies were analyzed for the number of adherent platelets over time. Shown are the mean ± SEM of 6 to 12 independent experiments (Supplementary Figure S4). Exponential fits yielded equilibrium coverages (95% CIs) of 4556 (4497-4615), 4233 (4160-4306), and 2545 (2352-2737) cells mm−2 for 0, 5, and 40 μM para-amino BBT, respectively. (B) Adhesion rate kon, fraction static, mean translocation velocity, and mean translocation distance of platelets adhering and rolling on VWF. Data were obtained by analysis of the same movies as in A. Error bars depict mean ± SEM. (C) Representative confocal images of platelets on fibrinogen-coated glass after 60 minutes of spreading at various BBT concentrations under static conditions. Green: f-actin; magenta: vinculin. Scale bars: 10 μm. (D) Confocal analysis of single-cell morphology in terms of (top to bottom) spreading area, circularity, f-actin alignment, the percentage of bipolar cells, and the average number of actin nodules per platelet. Mean values from 4 to 7 independent biological replicates with 262 to 564 cells per condition are shown. Error bars depict mean ± SEM. All statistical tests were performed using one-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons; only P values of <.05 are indicated.