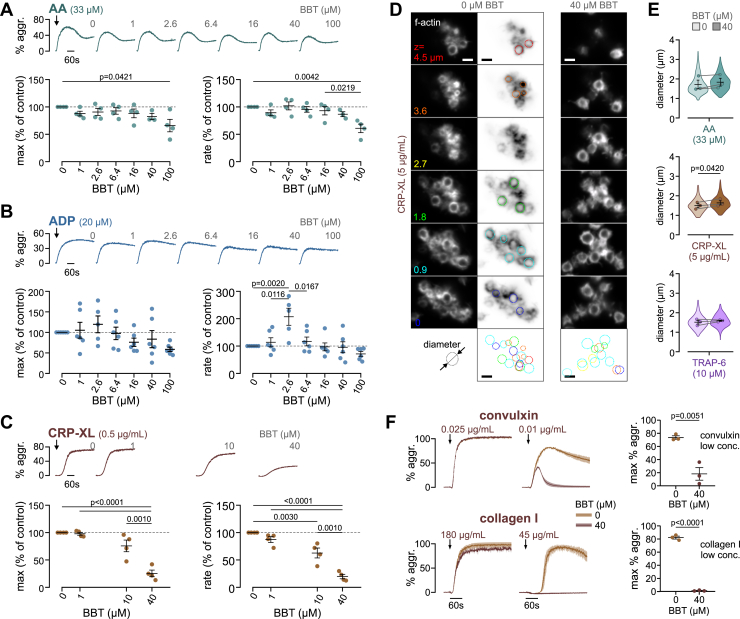
Figure 4.
The role of myosin IIA contractility in platelet aggregate formation depends on the activation pathway. Light transmission aggregometry of washed platelets preincubated with different para-amino blebbistatin (BBT) concentrations and stimulated by (A) arachidonic acid (AA), (B) adenosine diphosphate (ADP), or (C) crosslinked collagen-related peptide (CRP-XL). Shown are representative aggregation curves (top), maximum aggregation (left), and rate of aggregation (right) of 4 to 6 independent experiments. Values are shown normalized to control (0 μM BBT). Maximum aggregation in controls was (mean ± SD) 42.5 ± 5.3% for AA, 40.0 ± 6.2% for ADP, and 68.0 ± 6.8% for CRP-XL. Error bars depict the mean ± SEM. All statistical tests were performed using one-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons; only P values of <.05 are indicated. (D) Aggregates formed from washed platelets were fixed when reaching 30% aggregation, stained for f-actin, and imaged by confocal microscopy. Z-stacks of example aggregates formed using 5 μg/mL CRP-XL at 0 μM or 40 μM BBT. The diameter of platelets in the aggregate was determined by manual measurements from confocal slices (dashed-colored outlines). Scale bars: 2 μm. (E) Violin plots and means ± SEM of average platelet diameters per experimental replicate (points) from aggregates formed by AA (top), CRP-XL (middle), or thrombin receptor activating peptide-6 (TRAP-6; bottom) in the absence/presence of 40 μM BBT. Violin plots comprise 47 to 224 platelets from 12 to 16 aggregates from 3 experimental replicates per condition. Statistical comparisons were performed using a paired Student’s t-test. (F) Aggregation curves of washed platelets stimulated with saturating (left) or subsaturating (middle) concentrations of convulxin (top) or collagen type I (bottom). Curves show the mean and range of 2 technical replicates representative of 3 independent experiments. Right: maximum percent aggregation at low agonist concentrations for 3 independent experiments. Statistical comparisons were performed using an unpaired Student’s t-test.