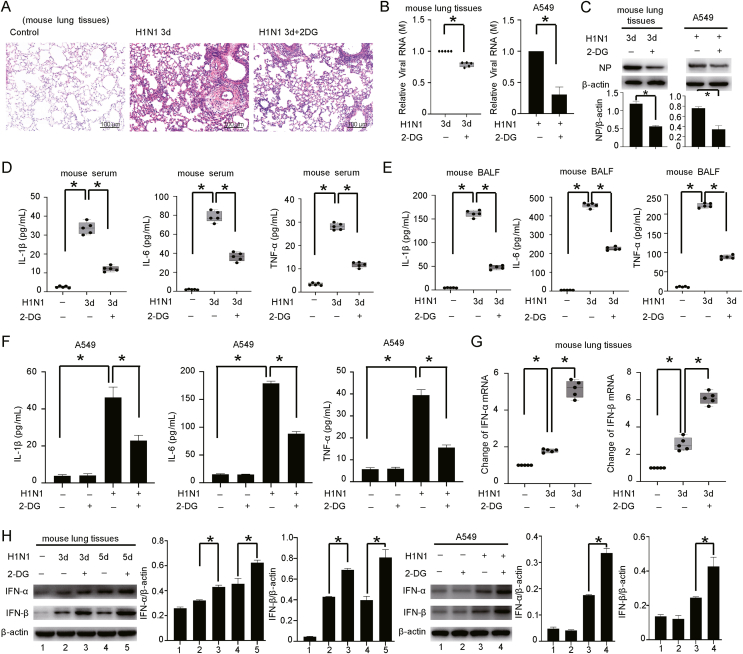
Fig. 4.
Inhibiting glycolysis attenuates H1N1-induced lung injury. A HE staining of lung tissues from H1N1-infected mice (n = 5, 1000 pfu per mouse) treated with or without 2-DG by intraperitoneal injection (500 mg/kg, once daily for 3 days). Scale bar = 100 μm. B, C The expression levels of M mRNA and NP protein in lung tissues (n = 5, 1000 pfu per mouse) and A549 cells (MOI = 1 for 24 h) infected with H1N1 virus and treated with or without 2-DG (10 mmol/L for 48 h for A549) were measured by qPCR and Western blotting. β-Actin served as the loading control. D, E The concentrations of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α in the serum and BALF of H1N1-infected mice after treatment with or without 2-DG (n = 5, 1000 pfu per mouse) were measured by ELISA. F The concentrations of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α in the culture supernatant of H1N1-infected A549 cells treated with or without 2-DG (10 mmol/L for 48 h) were measured by ELISA. G, H The expression of IFN-α/β in lung tissues of H1N1-infected mice (n = 5, 1000 pfu per mouse) or A549 cells (MOI = 1 for 24 h) treated with or without 2-DG (10 mmol/L for 48 h for A549) was evaluated by qPCR and Western blotting. β-Actin served as the loading control. The data are presented as the means with SDs. Statistical analysis was performed by Student's t-test and one-way ANOVA. ∗P < 0.05.