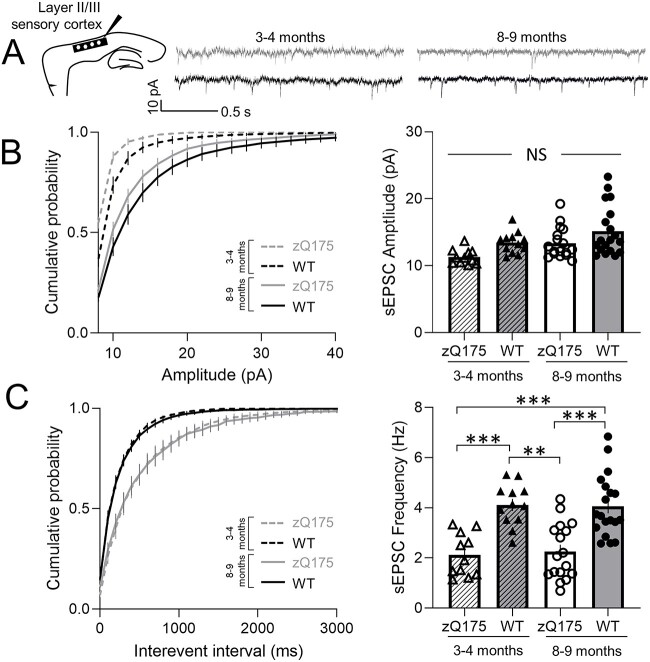
Figure 1.
Excitatory synaptic transmission of sensory cortical pyramidal neurons is reduced in zQ175 mice. (A) Representative traces of spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSCs) recorded from sensory cortical pyramidal neurons (CPNs) at 3–4 and 8–9 months for wildtype (WT) and zQ175 mice at a holding potential of −70 mV. (B and C) Cumulative probability of amplitude (B left panel) and frequency (C left panel) with corresponding mean amplitude (B right panel) and frequency (C right panel) (n = 11–19 from 4–5 mice for each group). Error bars denote SE. **, *** and NS denotes P < 0.01, 0.005 and statistically non-significant, respectively.