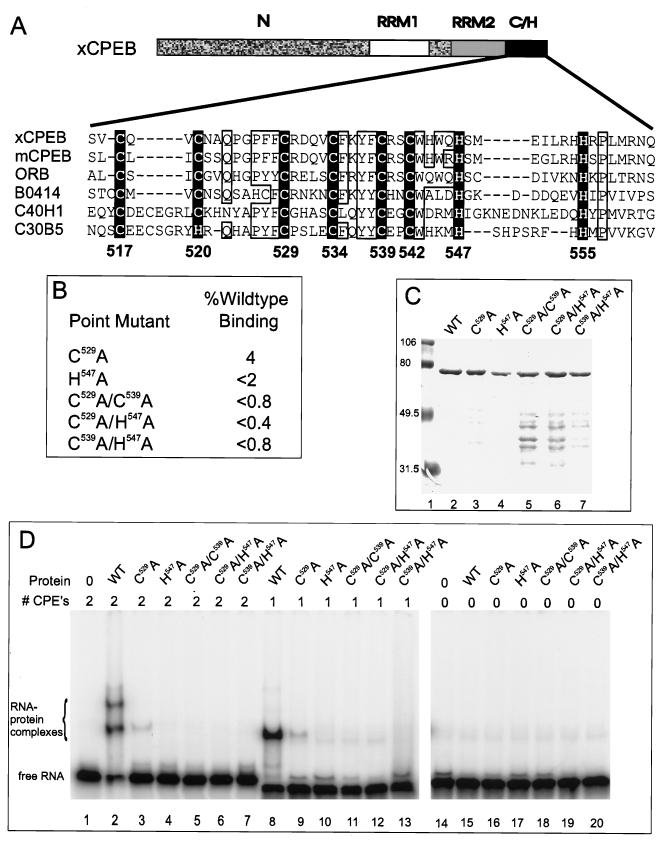
FIG. 4.
Mapping the RNA binding domain: effect of substituting cysteine and histidine residues with alanine. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of the cysteine-histidine region among CPEB homologs. xCPEB, Xenopus CPEB (accession no. u14169); mCPEB, mouse CPEB (accession no. Y08260); ORB, Drosophila ORB (accession no. X64412); three open reading frames from C. elegans with unknown function: B0414 (accession number AF003145), C40H1 (accession no. Z19154), and C30B5 (accession no. U23450). Conserved cysteine and histidine residues are in white inside a black box. Numbers below the boxes denote positions of amino acids in xCPEB. Note the additional conservation (open boxes) of glutamine (Q), proline (P), aromatic residues (phenylalanine [F], tyrosine [Y], and tryptophan [W]), and basic residues (arginine [R] and lysine [K]). (B) Point mutant clones containing alanine substitutions for specific residues and effects of these mutations on RNA binding expressed as a percentage of wild-type CPEB binding. C529A indicates that C529 was replaced with an alanine, etc. (C) Coomassie blue-stained SDS-polyacrylamide gel of mutant CPEBs used in RNA gel shift analyses. Protein standards are indicated to the left. WT, wild type. (D) RNA gel shift of radiolabeled B1wt RNA (lanes 1 to 7), B1cpe1 RNA (lanes 8 to 13), or B1cpe0 (lanes 14 to 20) incubated with 1 pmol of various CPEBs.