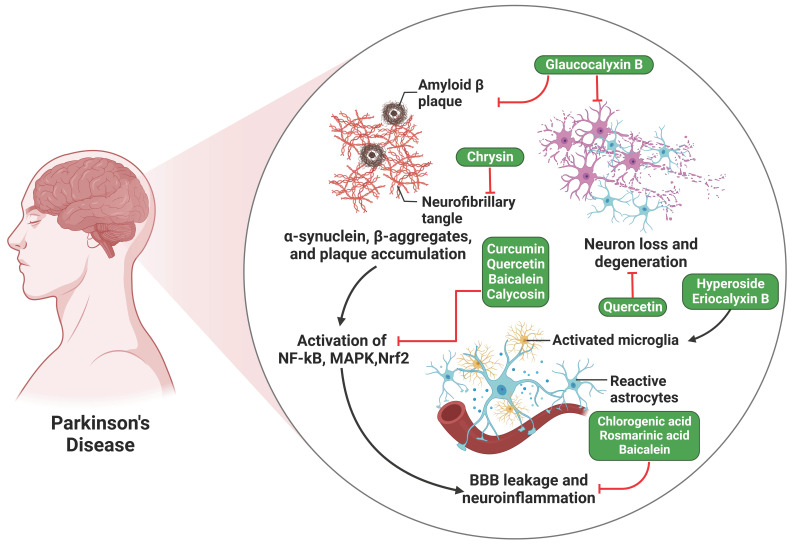
Figure 2.
Illustration represents the polyphenols targeting the NF-κB pathway associated with Parkinson's disease. The activation of the NF-κB, MAPK, and Nrf2 pathways by amyloid-beta plaque and neurofibrillary tangles ultimately results in the leaking of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and neuroinflammation, which ultimately leads to Parkinson's disease.