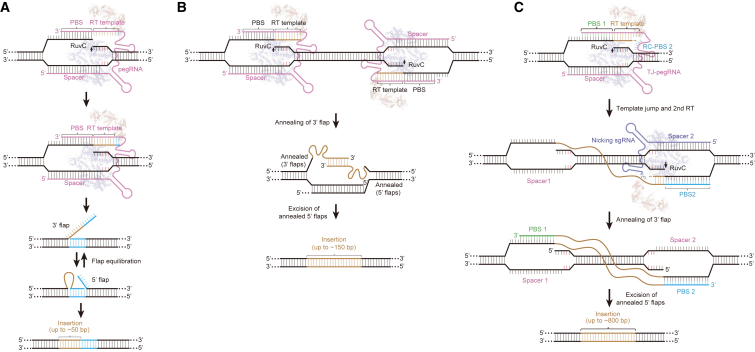
Figure 3.
Schematic overview of prime editing and paired prime editing
(A) Overview of prime editing. A prime editing complex consists of a prime editor (an RNA-guided DNA nicking domain, such as Cas9 nickase, fused to and reverse transcriptase domain) and a pegRNA. The prime editing complex binds the target DNA and nicks the non-target strand, and the resulting 3′ end hybridizes to the PBS sequence, then initiates reverse transcription of new DNA containing the desired insertion fragment (up to ∼50 bp) using the template of the pegRNA. Equilibration between the edited 3′ flap and the unedited 5′ flap, excision of the unedited 5′ flap, and DNA repair results in stably edited DNA. (B) Overview of paired prime editing. Prime editing with paired pegRNAs that template two 3′ DNA flaps containing the edit. Annealing of the fully or partially complementary flaps, excision of the original genomic duplex, and DNA repair mediates large DNA fragment insertion (∼1 kb). (C) Schematic of TJ-PE. In contrast with pegRNA designed for prime editing, the TJ-pegRNA consists of two PBSs, which initiates two rounds of reverse transcription sequentially thus enabling insertion of long external DNA (up to ∼800 bp). RT template, reverse transcription template.