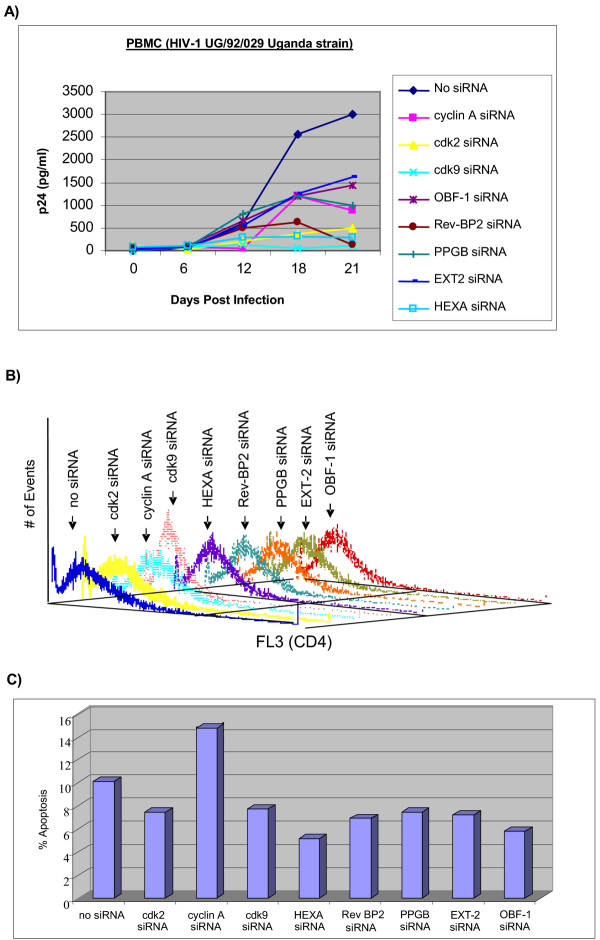
Figure 7.
Effect of representative siRNA treatment in PBMC field isolate HIV-1 infection. Approximately 5 × 106 Phytohemagglutinin-activated PBMC were kept in culture for two days prior to infection. PBMC were first treated for 48 hrs with 10 μg of the various siRNAs and then infected with SI (UG/92/029 Uganda strain, subtype A envelope, 5 ng of p24 gag antigen) strain of HIV-1 obtained from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) AIDS Research and Reference Reagent Program. After 8 h of infection, cells were washed and fresh media was added. Samples were collected every sixth day and stored at -20°C for p24 gag enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Media from infected cell lines was centrifuged to pellet the cells and supernatants were collected and diluted to 1:100 to 1:1,000 in RPMI 1640 prior to analysis. Supernatants from the infected PBMC were collected and used directly for the p24 antigen assay. The p24 gag antigen level was analyzed using the HIVAG-1 Monoclonal Antibody Kit (Abbott Laboratories, Diagnostics Division). (B) PBMCs stimulated with PHA were treated with appropriate siRNA prior to HIV infection and stained for presence of surface CD4 on activated cells. Prior to infection, 1/5 of the samples were processed for CD4 and PI staining. Cells were then collected and washed twice with PBS containing FCS and NaN3. Cells were stained on ice for with human tri-color-labeled anti-CD4 (Catalog Laboratories) at a 1:10 dilution. Stained cells were next washed two times in PBS containing FCS and NaN3 and fixed in paraformaldehyde followed by analysis by FACS. (C) FACS analysis of PI stained cells from panel B. Sub-G1 population was scored as apoptotic population in each siRNA treated cell.