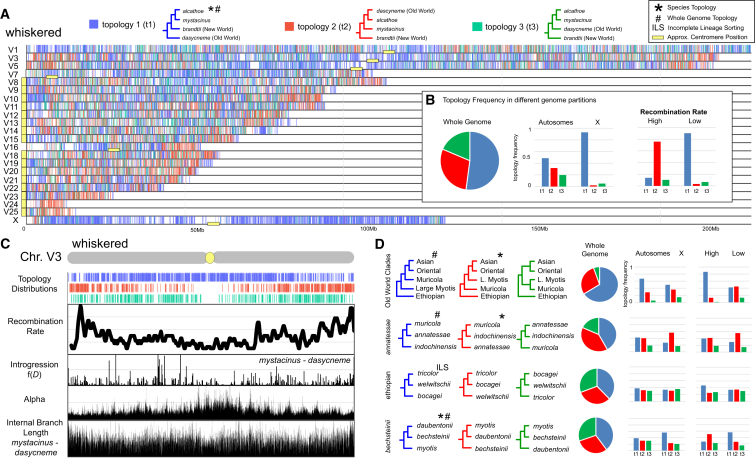
Figure 3.
Genome-wide distribution of phylogenomic discordance across the Old World Myotis radiation
(A) Distribution of phylogenomic signal for the whiskered clade visualized using Tree House Explorer61 in 50 kb locus alignment windows across the genome. Vertical bars along each chromosome are color coded to depict the distribution of the most frequent topologies.
(B) Comparison of the frequency of t1, t2, and t3 across the whole genome (left) and between the autosomes and the X (middle) and between high and low recombining regions of the genome (right).
(C) Whole-chromosome view for ChrV3 illustrates local relationship between recombination rate, f(D), the alpha parameter of the gamma model, and the internal branch length (ibl) for relationships between M. mystacinus and M. dasycneme. Note the depletion of topologies associated with introgression (t2 [red], t3 [green]) in the low recombining region at the center of the chromosome.
(D) Distributions of phylogenomic signal for additional Myotis clades in relation to chromosome type and recombination rate (reference the key in B).